In the case of Goods and Services Tax (GST) registration as a sole proprietorship requires careful attention to documentation. In the complicated process of financial compliance, having a clear understanding of the necessary paperwork is the primary concern.
This blog aims to demystify the process, offering a straightforward guide on the essential documents required for GST registration for sole proprietorships.
Whether you’re a growing entrepreneur or an established business owner, ensuring you have the right paperwork in order is the first step toward seamless GST compliance.
Let’s delve into the specifics, opening the complications of documentation in the reality of sole proprietorship GST registration.
Introduction to GST Registration for Sole Proprietorship
Goods and Services Tax (GST) registration is a crucial step for sole proprietors, marking their entry into the structured tax system. Essentially, GST is a consumption-based tax that replaces multiple indirect taxes. For sole proprietors, this registration is necessary once their aggregate turnover surpasses the prescribed threshold.
In the context of financial transactions, GST aims to streamline the taxation process, providing a unified platform for businesses. This formal registration ensures that the government can track and regulate the flow of goods and services, facilitating transparency in the business ecosystem.
For sole proprietors, navigating the intricacies of GST registration requires a clear understanding of the financial obligations and documentation involved. It’s a means to establish compliance with tax regulations and enjoy the benefits of a simplified and standardized tax framework.
Furthermore, GST registration opens doors to various advantages, such as input tax credits, which allow businesses to offset taxes paid on inputs against their final tax liability. This mechanism contributes to the overall ease of doing business, promoting a more efficient and equitable taxation system. Additionally, it aligns businesses with global standards, enhancing their competitiveness in the broader marketplace.
Advantages of GST Registration for Sole Proprietorship
Goods and Services Tax (GST) registration for a Sole Proprietorship offers several advantages, particularly from a financial perspective. Here are some key points to consider:
- Legitimacy and Compliance: GST registration imparts a sense of legitimacy to the business. being a registered entity showcases compliance with tax regulations, fostering trust among clients, suppliers, and financial institutions.
- Input Tax Credit (ITC): Eligibility for claiming ITC on input taxes paid. A registered sole proprietor can offset the GST paid on purchases against the GST collected on sales, reducing the overall tax liability and improving profitability.
- Legal Recourse: Access to legal remedies in case of disputes. A GST-registered sole proprietor has a legal standing, enabling recourse through appropriate channels in case of disputes related to taxation or business transactions.
- Government Tenders and Contracts: Eligibility for government tenders and contracts. Many government bodies and large corporations mandate GST registration for vendors, making it a prerequisite for participating in tenders and securing contracts.
- Ease of Doing Business: Simplified tax compliance processes. GST streamlines the tax compliance landscape by replacing multiple indirect taxes, making it easier for sole proprietors to manage their tax obligations efficiently.
GST registration for a sole proprietorship brings about several financial advantages, including cost savings through ITC, improved market standing, and access to a wider range of business opportunities.
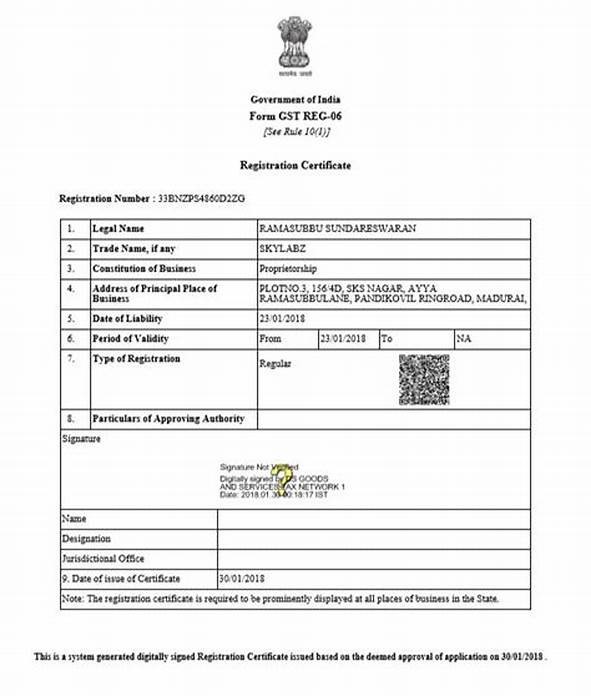
The Process of GST Registration for Sole Proprietorship
GST registration for a sole proprietorship is a crucial undertaking, blending simplicity with financial prudence. In this segment, we will demystify the process:
- Preparation and Documentation: Begin by gathering the necessary documents for GST registration such as PAN card, Aadhar card, bank statements, and business address proof. Ensure that all financial records are to facilitate a smooth application process
- Online Application: Visit the official GST portal (www.gst.gov.in) and navigate to the ‘Services’ section. Click on ‘New Registration’ and fill in the required details in the online application form. Provide accurate information regarding business details, promoters, and the type of business activity.
- Verification through OTP: Once the application is submitted, the mobile number and email ID provided will undergo verification through a One-Time Password (OTP). Ensure that these contact details are accurate and accessible during the registration process.
- Submission of Documents: Upload the scanned copies of the required documents on the GST portal. This includes proof of business ownership, address verification, and the proprietor’s identity documents. The documents will be scrutinized by the authorities for authenticity.
- Verification by GST Officer: The GST officer will review the application and documents. If any discrepancies or additional information is required, they may reach out for clarification. Once satisfied, the officer will approve the application.
- Issuance of GSTIN: Upon successful verification, the Goods and Services Tax Identification Number (GSTIN) will be generated and issued to the sole proprietor. This unique 15-digit number serves as the identification for the business under the GST regime.
- Compliance and Filing: Post-registration, the sole proprietor is required to comply with regular GST filing obligations. This includes filing monthly, quarterly, or annual returns, depending on the turnover and nature of the business.
- Display of GSTIN: The GSTIN should be prominently displayed at the place of business. This helps in establishing the business’s GST compliance and legitimacy.
- ITC Claim: After registration, the sole proprietor can start claiming Input Tax Credit (ITC) on eligible purchases, thereby optimizing their tax liability.
The GST registration process for a sole proprietorship involves the submission of relevant documents, online application, verification, and the subsequent issuance of GSTIN.
Documents Required for GST Registration
Documents required for GST registration for a sole proprietorship is a crucial undertaking, blending simplicity with financial prudence. In this segment, we will demystify the process:
| Identity and Address Proof of Proprietor | Provide a scanned copy of the proprietor’s documents like PAN card, Aadhar card, passport-sized photograph, and residential address proof. This establishes the identity and residential address of the business owner. |
| Business Proof | Submit documents verifying the existence of the sole proprietorship, such as the business registration certificate, partnership deed, or any other applicable business proof. |
| Address Proof for Place of Business | Furnish documents confirming the address of the business premises, such as rent agreements, utility bills, or property tax receipts. |
| Bank Statements or Passbook | Provide the bank statement or passbook of the business’s primary bank account, showcasing the name of the business, address, and the first few pages that reflect transactions. |
| Authorization Letter | If the proprietor is unable to apply personally, an authorization letter granting permission to an authorized signatory along with their identity proof should be provided. |
| Photographs | Submit passport-sized photographs of the proprietor to be affixed to the GST registration application form. |
| Digital Signature | A digital signature is required for certain categories of businesses. If applicable, provide the digital signature certificate. |
| Business Activities Proof | Documents required for substantiating the nature of business activities, such as invoices, agreements, or any other relevant proof. |
Ensuring that all these documents are accurate, up-to-date, and submitted in the prescribed format is crucial for a smooth GST registration for the sole proprietor process.
Understanding Each Document’s Importance
Each and every document is important while registering the GST process, let’s talk one by one:
- Identity and Address Proof of Proprietor:
- Importance: This establishes the legal identity and residential address of the sole proprietor. Essential for verifying the authenticity of the business owner.
- Business Proof:
- Importance: It helps validate the existence of the sole proprietorship. It can be in the form of a registration certificate, partnership deed, or any other relevant document confirming the business structure.
- Address Proof for Place of Business:
- Importance: Confirms the physical location of the business. This document, such as a rent agreement or utility bill, provides evidence of the business’s operational address.
- Bank Statements or Passbook:
- Importance: Offers insights into the financial transactions of the business. It serves as evidence of a valid business bank account and provides essential financial information.
- Authorization Letter:
- Importance: To grant permission for an authorized signatory to apply on behalf of the proprietor. Necessary if the proprietor is unable to apply personally, ensuring a legal representation in the registration process.
- Photographs:
- Importance: Adds a visual confirmation of the proprietor’s identity. Passport-sized photographs are affixed to the application form, contributing to the overall verification process.
- Digital Signature:
- Importance: Required for certain categories of businesses. The digital signature ensures the authenticity of the electronic documents submitted during the registration process.
- Business Activities Proof:
- Importance: Substantiates the nature of the business activities. Invoices, agreements, or other relevant documents provide evidence of the products or services offered by the sole proprietorship.
Understanding the importance of each document is vital for a successful GST registration process. Together, these documents create a comprehensive profile of the sole proprietorship.
Conclusion
In conclusion, navigating the GST registration process for a sole proprietorship involves meticulous steps, from document preparation to the issuance of the GSTIN. The seamless online application, verification, and subsequent compliance procedures pave the way for a simplified taxation system.
This process not only signifies regulatory adherence but unlocks opportunities for market competitiveness, eligibility for government tenders, and streamlined financial operations.
In embracing GST, the registration process for a sole proprietorship ensures a credible, compliant, and growth-oriented presence in the dynamic business landscape.
FAQs
Q1: Why is GST registration essential for a sole proprietorship?
GST registration establishes the business’s legitimacy, enhances market competitiveness, and allows access to Input Tax Credit (ITC) benefits.
Q2: What documents are crucial for GST registration?
Key documents include PAN card, Aadhar card, business proof, address proof, bank statements, and digital signature (if applicable).
Q3: Can a sole proprietor appoint an authorized signatory for GST registration?
Yes, a proprietor can authorize someone to apply on their behalf with a duly signed authorization letter and the authorized signatory’s identity proof.
Q4: How long does it take to complete the GST registration process?
The timeline varies, but typically, the process takes a few working days, subject to document verification and officer approval.
Q5: What is a GSTIN, and why is it important?
GSTIN is the unique 15-digit Goods and Services Tax Identification Number. It is crucial for identifying and conducting transactions within the GST framework.
Q6: Is GST registration mandatory for all sole proprietorships?
It is mandatory for businesses with an aggregate turnover exceeding the threshold limit, as specified by the GST authorities.
Q7: Can a sole proprietor claim Input Tax Credit (ITC) after GST registration?
Yes, GST-registered sole proprietors can claim ITC on eligible purchases, reducing their overall tax liability.
Q8: What are the repercussions of not obtaining GST registration?
Operating without GST registration may lead to legal consequences, penalties, and exclusion from various business opportunities.
Q9: How often does a sole proprietor need to file GST returns?
The frequency of filing returns depends on the turnover and nature of the business—monthly, quarterly, or annually.
Q10: Can a sole proprietorship apply for GST registration online?
Yes, the entire GST registration process, including application submission and document uploads, can be completed online through the official GST portal.