It’s every taxpayer’s responsibility to stay compliant with the Goods and Services Tax regulations. The taxation regime is constantly changing as the GST council develops new rules, notifications, forms, and amendments to enhance the customs filling process from registration to filling. Goods and Service Tax Identification Number (GSTIN) is one of India’s most essential pieces of the tax regulation puzzle.
Understanding GSTIN
GSTIN is an identification number commonly assigned to every business registered under the GST regime in India. It consists of a 15-digit alphanumeric that helps in the registration process and helps companies stay compliant with GST regulations.
Since its inception in 2017, the GSTIN number has been used to simplify the taxation process, thereby creating a unified tax structure. The 15 alphanumeric codes are divided into five components:
The chart below from Saginfotech shows GSTIN representation
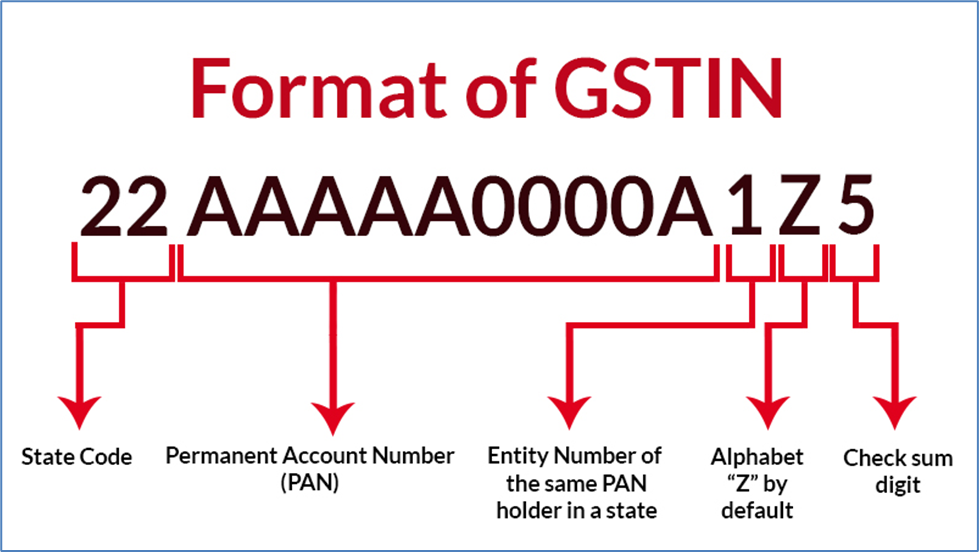
Source: Saginfotech.com
- First two digits of GSTIN represent the state code. Each state has a unique code assigned to it for accurate identification.
- The next ten digits: Comprise the permanent account number of the business entity. The digits help identify a business involved in a given transaction.
- The thirteenth digit of GSTIN: Echoes the entity type of the business, such as proprietorship, partnership, company, etc.
- The fourteenth digit of GSTIN: left blank for future use.
- Fifteenth digit of GSTIN: The fifteenth digit of the GSTIN is a check code used to detect errors.
GSTIN was explicitly designed to provide legal recognition to businesses while ensuring they comply with GST regulations. For starters, it allows businesses to claim input tax credits for purchases and settle off the tax-paid inputs against tax liability.
In the supply chain network, the 15 alphanumeric codes play an important role in tracking the movement of goods, thus ensuring seamless tax compliance across state borders. On the other hand e, e-commerce platforms require sellers to have GSTIN as it enhances the verification of whatever they are selling while ensuring compliance with tax regulations.
GSTIN Complexities
While the Goods and Services Tax Council constantly updates the tax framework with new regulations and updates, staying compliant is always a challenge right from the GSTIN registration process to the final process of paying tax or claiming an input tax credit; many businesses and taxpayers are often caught off-guard given the changes that come into play.
The intricacies in between the constant updates have made it difficult for businesses and new taxpayers joining the fold to stay compliant. The risk of being hit with hefty penalties for failing to adhere to the tax filing regulations is increasingly pilling up, dragging most people and businesses into the abyss.
Since its inception in 2017, over 740 notifications have been issued, with 395 touching on the central tax notifications. In addition, there have been over 140 central tax rate notifications that have caught some businesses unaware. It is not a surprise that the complexity of the GSTIN tax structure could make many companies unable to cope with the punitive regulatory structure that keeps changing.
GSTIN complexities start right from the registration process, whereby businesses and individuals must register to purchase or sell goods and render services. When faced with any complexity or standoff, one might need help to navigate.
GSTIN Registration Complexities
One of the complexities tied to GSTIN registration revolves around understanding the different GST types and their associated rates. India’s tax regime follows a dual taxation model whereby the state and central government have authority over collecting taxes.
Given that both are involved in the collection process using the GSTIN, it presents unique challenges and complexities. There are three types of GST fillings that any taxpayer in India should have a good understanding of. They are:
- CGST
- SGST
- IGST
Also Read: How to Register for GST and Obtain Your GSTIN Number?
Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST)
Central Goods and Services Tax is a tax rate imposed by the central government on the interstate supply of services and goods. In this case, every revenue collected ends up to the central government. One of the complexities of the various rules that govern CGST includes:
- Businesses under the Composition Scheme are required by law to provide a supply bill for all goods transacted and services rendered.
- Registered businesses must issue tax invoices on all tax invoices for goods and services, each coming with a unique identifiable serial number.
- Equal CGST and SGST may be levied, leading to a combined GST rate, i.e., an 18% GST rate and a 9% SGST rate for a combined 18% GST rate.
For businesses and taxpayers to comply with the CGST regulations, they must furnish the tax agency with the following documents.
- A duly filled application for CSGT registration
- A Permanent Account Number PAN that serves as a unique identification for tax purposes
- Aadhaar Card for proof of identity
- One must also provide a cheque leaf needed for bank account verification
- A valid document showing proof of business location
The required rules and documents add to the complications of the GSTIN registration process that continues to bar many businesses and individuals from joining the tax bracket.
State Goods and Services Tax (SGST)
It is one of the most critical aspects of India’s GST system that details the rate that the state government charges on intra-state transactions. The state government charges an SGST on all intrastate transactions for goods and services and the taxable value of the supply. It includes the costs of goods or services and other additional charges for packaging, freight, insurance, and other taxes.
The framework came into being as one of the ways of replacing the complex and varied state-level taxes with a simplified tax structure. The tax rate charged by the state government goes into the respective state governments and helps eliminate the need for multiple state-level taxes.
SGST has helped reduce the compliance burdens and administrative complexities that were in place in the past by ensuring uniform tax rates within each state. Therefore, it has helped promote consistency and transparency in taxation while boosting state revenues generated through the SGST collections.
Also Read: State Goods And Service Tax (SGST)
Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST)
It is a tax imposed by the central governments billed on all the interstate supply of goods and services. All the revenue collected by this framework is shared between the state and the central government. The IGST applies to the transactions that involve the movement of goods and services between two states, including union territories. Therefore, it is designed to ensure uniformity in taxation for interstate movements while eliminating the complexities of multiple state tax rates.
The GST council is mandated to provide a uniform IGST rate consistent across all the states, averting the risk of ambiguity or varying tax rates. Businesses that incur an IGST bill are eligible to claim an input tax. In the case of interstate transactions, sellers must bill IGST on the invoice. In return, the buyer must pay the applicable amount, and the seller remits the necessary taxes to the government.
In addition, the buyer and seller must have a valid GSTIN for seamless compliance with all the regulations. Additionally, IGST applies to goods and services imported into or exported from the country. The tax arrangement will always depend on whether it is an import or export transaction.
E-commerce businesses operating across state lines must be the most diligent in the GST process. They must register in all the states they use to pay the applicable IGST rate on the goods and services they transact. The complexities of calculating the necessary GST one commerce sales call for extra attention to detail and understanding of the various tax exemptions.
In this case, an e-commerce business can circumvent the complexities by simply:
- Identifying the tax rate applicable to each item they sell.
- Getting the facts right on the place of supply for goods or services
- Calculate the applicable rate depending on the type of transaction (CGST + SGST/UTGST for intra-state and IGST for inter-state).
- Ensure accurate GST-compliant invoices are issued to customers while mentioning all required details like GSTIN, HSN/SAC codes, and the tax amount.
GSTIN Documentation Complexities
Another complexity of GSTIN registration relates to the documentation required to complete the process. Businesses must avail a wide array of documents, from PAN cards to bank account details and Aadhaar cards, among others, to complete the registration process.
Gathering and submitting the documents is a challenging feat, especially for businesses that are just starting up. The process can take a long time and have lots of challenges when one cannot locate all the required documents, let alone understand how to go about the entire process.
It’s for this reason that most businesses engage the services of professionals in the registration process. The professionals or consulting companies come in handy in providing various services that assist businesses in collecting and filing all the required documents. Therefore, one of the best practices involves engaging advisory services to access the much-needed resources to circumvent any complexity.
By partnering with a reputable GSTIN registration company, a business can access in-depth guidance and support needed to navigate the various challenges of the entire GSTIN registration process. In return, the partnership should ensure compliance with GST laws and regulations, leading to optimized financial performance, thus setting the business up for long-term success.
Also Read: Importance Of Keeping The GST Documentation Up-To-Date
Conclusion
GSTIN is one of the essential pieces of the GST system that ensures businesses comply with the country’s customs norms and requirements. While it is mandatory for all taxpayers who transact business across state laws, it comes with many complexities, from the registration process to the collection of the required documents for submission. Therefore, businesses are often encouraged to partner with reputable professionals who can provide much-needed guidance on addressing the various challenges.
In addition, various software solutions have been designed to help small businesses comply. The software tools are tailored to automate tedious compliance processes, from registration to invoice generation and return filing.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is GSTIN?
It is a 15-digit identification number given to every taxpayer or business entity registered under the GST. Obtaining the unique identification number does not cost anything and goes a long way in facilitating compliance with GST laws, rules, and regulations. It also makes it easier for businesses to file the necessary tax returns.
2. I am yet to receive GSTIN, can I supply goods or services or both?
Any taxpayer can supply goods, services, or both on an invoice without mentioning GSTIN. On receipt of GSTIN, you will need to issue a revised invoice mentioning GSTIN. A taxpayer must only reflect this supply in the return and pay the applicable tax. Any taxpayer with a provisional ID can supply goods or services awaiting the GSTIN issuance.
3. Who is required to register for GSTIN, and when?
Every entity that supplies goods and renders services for income is required to register for GSTIN. However, there are requirements for the registration process. For instance, registration in North Eastern states is for taxpayers who handle goods worth more than 10 Lakhs. For the rest of India, all people who handle goods worth more than Rs 20 Lakhs in services and 40 Lakhs in products must register.
4. Are there requirements for GSTR filling?
Yes, there are requirements that taxpayers must meet for proper tax filing. For starters, a taxpayer must have a valid GSTIN and login credentials. A taxpayer should also have an active DSC and use an e-sign if mandatory.
5. What are some of the requirements for the GSTIN registration?
Some of the requirements include:
- PAN Card and Aadhaar card where possible
- Digital Signature for companies and LLP
- Valid mobile number and Email address
- Photograph of Proprietor, partners, authorized signatories of a business being registered
- Registration Certificate validating the business obtained under earlier Tax laws.
- Proof of appointment of authorized signatory of the business and their details
- Proof of address detailing where the business is located
- Opening page of Bank statement held in the name of the business
