In taxes, businesses sometimes need to register as an Input Service Distributor (ISD). An ISD helps companies share tax credits between different parts of the business. For example, if a company has branches in different cities, an ISD makes sure each branch gets its fair share of tax credits. It’s like making sure everyone gets their slice of the pie. This registration is crucial for businesses that operate across multiple locations or engage in diverse activities, enabling them to effectively manage and allocate tax credits. By registering with an ISD, entities can streamline their tax processes, ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, and optimize their financial operations.
Let’s understand in detail, about Input Service Distributor (ISD)!
NRT GST registration for Input Service Distributors (ISDs)
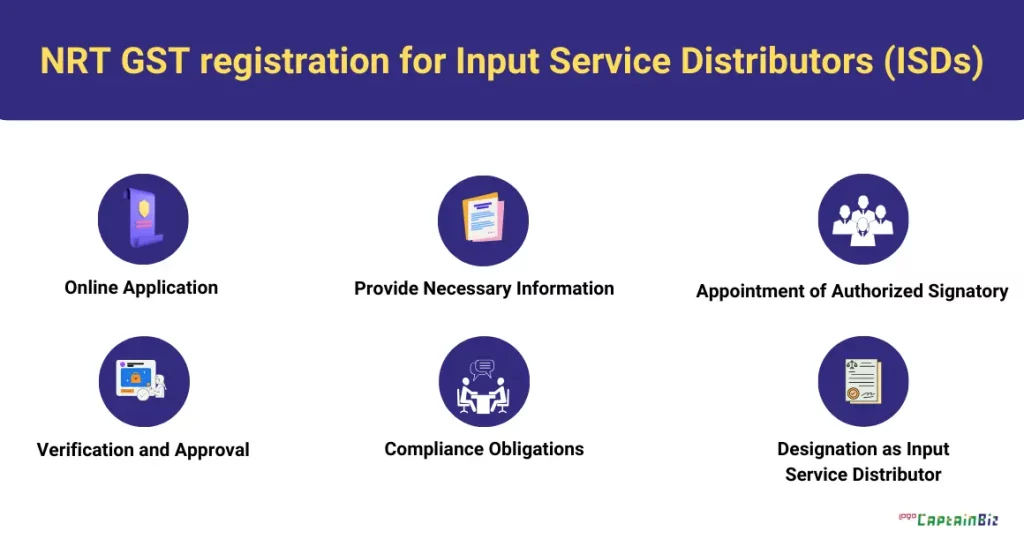
NRT GST registration for ISDs means Non-Resident Taxpayers registering as Input Service Distributors under GST. This allows non-resident entities to distribute input tax credits even if they don’t have a physical presence in the country..
The GST registration process for Input Service Distributors (ISDs) for non-residents in India follows similar steps as for resident entities, with a few considerations:
- Online Application: Non-resident entities can apply for GST registration online through the GST portal.
- Provide Necessary Information: The applicant needs to provide details such as business name, address, PAN (Permanent Account Number), and other required documents.
- Appointment of Authorized Signatory: A person resident in India needs to be appointed as an authorized signatory for GST compliance purposes.
- Verification and Approval: After submitting the application, the GST authorities verify the details provided. Once verified, GST registration is approved, and a GSTIN (Goods and Services Tax Identification Number) is issued.
- Compliance Obligations: Once registered, non-resident ISDs need to comply with GST regulations, including filing GST returns, maintaining proper records, and fulfilling other compliance requirements.
- Designation as Input Service Distributor: Upon registration, the non-resident entity can designate itself as an Input Service Distributor, enabling it to distribute input tax credits to its branches or units in India.
Eligibility criteria for NRT registration as an ISD
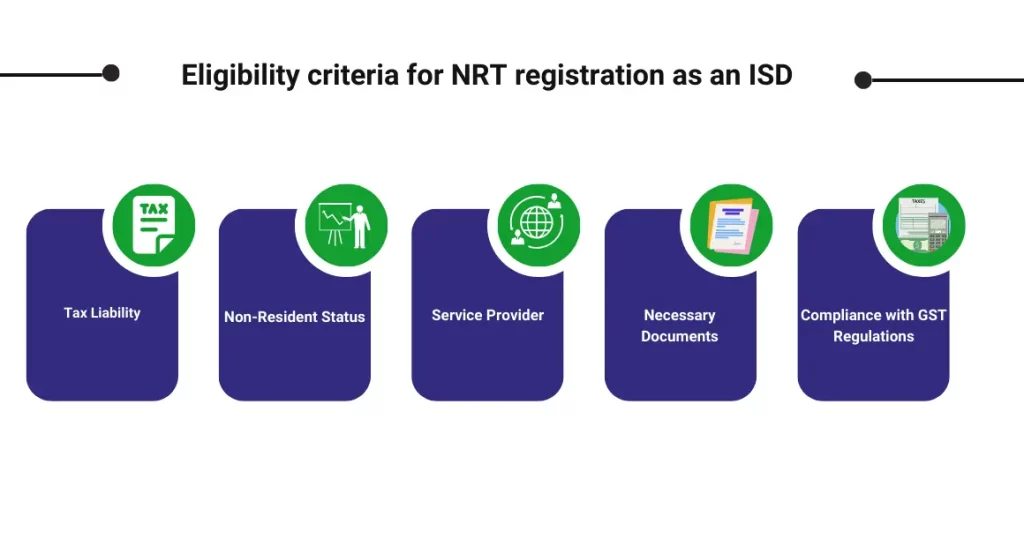
The eligibility criteria for Non-Resident Taxpayers (NRT) to register as Input Service Distributors (ISDs) typically include the following:
- Tax Liability: The entity must be liable to pay Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India for providing taxable services.
- Non-Resident Status: The entity should be a non-resident, meaning it does not have a physical presence or a fixed establishment in India.
- Service Provider: The entity should be engaged in providing services that are eligible for input tax credits under the GST regime.
- Necessary Documents: The entity must submit all required documents and information as specified by the GST authorities during the registration process.
- Compliance with GST Regulations: The entity should agree to comply with all GST regulations, including filing returns, maintaining records, and adhering to other compliance obligations.
Special requirements and procedures for NRT ISD registration

The special requirements and procedures for Non-Resident Taxpayer (NRT) Input Service Distributor (ISD) registration may vary slightly from those applicable to resident entities. Here are some potential special considerations:
- Authorization of Local Representative: Non-resident entities may need to appoint a local representative or agent who can act on their behalf for GST-related matters in India.
- Verification of Non-resident Status: The GST authorities may require additional verification to confirm the non-resident status of the entity, which could involve submitting proof of residency status from the entity’s home country.
- Submission of Additional Documentation: Non-resident entities may need to provide additional documentation or information to demonstrate their eligibility for ISD registration and compliance with GST regulations.
- Online Application Process: The registration process for NRT ISDs may involve an online application through the GST portal, similar to resident entities, but with specific fields or requirements tailored to non-resident taxpayers.
- Clearance from Relevant Authorities: Depending on the nature of the business and the countries involved, non-resident entities may need to obtain clearance or approval from relevant authorities, such as tax authorities in their home country or regulatory bodies in India.
- Designation of Local Contact Person: Non-resident ISDs may need to designate a local contact person or liaison who can communicate with the GST authorities and fulfill other compliance obligations as required.
These special requirements and procedures aim to ensure that non-resident entities can register as ISDs in compliance with GST regulations, despite their unique circumstances and geographical location.
Tax implications and compliance obligations for NRT ISDs
The tax implications and compliance obligations for Non-Resident Taxpayer (NRT) Input Service Distributors (ISDs) under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) system may include the following:
- Tax Liability: NRT ISDs are liable to pay GST on the services they provide in India, subject to the applicable rates and exemptions.
- Input Tax Credits (ITC): NRT ISDs can claim input tax credits for GST paid on eligible inputs and input services used in the course of their business activities in India.
- Compliance with Filing Requirements: NRT ISDs must file GST returns periodically, as prescribed by the GST authorities, providing details of their taxable supplies, input tax credits, and tax liabilities.
- Maintenance of Records: NRT ISDs are required to maintain proper records of their business transactions, including invoices, accounts, and other relevant documents, in accordance with GST regulations.
- Appointment of Authorized Signatory: NRT ISDs must appoint a person resident in India as their authorized signatory for GST compliance purposes, who will be responsible for filing returns and other regulatory requirements.
- Audit and Assessment: NRT ISDs may be subject to GST audits and assessments by the tax authorities to verify their compliance with GST regulations and assess any tax liabilities.
- Penalties for Non-Compliance: Failure to comply with GST regulations, such as late filing of returns or incorrect reporting, may result in penalties or other enforcement actions by the tax authorities.
Overall, NRT ISDs must ensure strict adherence to GST compliance requirements to avoid any adverse tax implications or penalties. Proper record-keeping and timely filing of returns are essential to maintain compliance with GST regulations.
Role of NRT ISDs in the GST supply chain
The role of Non-Resident Taxpayer (NRT) Input Service Distributors (ISDs) in the GST (Goods and Services Tax) supply chain is to facilitate the distribution of input tax credits (ITCs) among various branches or units of a company. Here’s how NRT ISDs contribute to the GST supply chain:
- Centralized Tax Credit Distribution: NRT ISDs act as centralized entities responsible for distributing input tax credits accrued from the procurement of input services across different branches or units of a company.
- Efficient Allocation of Resources: By consolidating and distributing input tax credits, NRT ISDs ensure that each branch or unit receives its fair share of credits, optimizing the utilization of resources within the organization.
- Streamlined Compliance: NRT ISDs help streamline GST compliance by centralizing the process of claiming and distributing input tax credits, reducing the administrative burden on individual branches or units.
- Cost Savings: Centralized input tax credit distribution by NRT ISDs can lead to cost savings for the organization by minimizing the duplication of efforts and maximizing the utilization of available credits.
- Enhanced Control and Oversight: NRT ISDs provide greater control and oversight over the utilization of input tax credits within the organization, ensuring compliance with GST regulations and minimizing the risk of non-compliance.
Overall, the role of NRT ISDs in the GST supply chain is to facilitate efficient tax credit management and compliance across geographically dispersed operations, contributing to the smooth functioning of the organization’s business activities within the GST framework.
Managing NRT ISD registration and compliance effectively
Managing Non-Resident Taxpayer (NRT) Input Service Distributor (ISD) registration and compliance effectively involves several key steps:
- Understanding Regulatory Requirements: Stay updated on the latest GST regulations and guidelines applicable to NRT ISDs to ensure compliance with all legal requirements.
- Appointing a Local Representative: Nominate a reliable local representative or agent in India who can act on behalf of the NRT ISD for GST-related matters and serve as the authorized signatory for compliance purposes.
- Thorough Documentation: Maintain comprehensive records of all transactions, invoices, and other relevant documents to support GST compliance and facilitate the filing of accurate returns.
- Regular Review and Monitoring: Conduct periodic reviews and audits of the NRT ISD’s GST compliance processes to identify any potential issues or areas for improvement and take corrective action as necessary.
- Training and Awareness: Provide training and awareness programs for relevant personnel involved in GST compliance to ensure they understand their responsibilities and are equipped to fulfill them effectively.
- Utilizing Technology: Leverage technology solutions such as GST-compliant accounting software to streamline compliance processes, automate data entry, and generate accurate reports for filing GST returns.
- Engaging Professional Expertise: Consider engaging the services of qualified tax professionals or consultants with expertise in GST compliance to provide guidance and support in managing NRT ISD registration and compliance effectively.
- Timely Filing of Returns: Ensure timely filing of GST returns and payment of taxes to avoid penalties or other enforcement actions by the tax authorities.
By implementing these strategies, NRT ISDs can effectively manage their registration and compliance obligations under the GST framework, minimizing the risk of non-compliance and ensuring smooth operations within the regulatory framework.
Conclusion
In conclusion, registering as an Input Service Distributor (ISD) comes with special considerations, especially for Non-Resident Taxpayers (NRT). From getting registered for NRT GST to meeting eligibility criteria, following specific procedures, and understanding tax implications, every step is crucial. NRT ISDs play a key role in the GST supply chain, and effective management of registration and compliance is essential. By staying organized and meeting requirements, NRT ISDs can ensure smooth operations within the GST framework.
Also Read: What Are The Benefits Of Integrating GST Registration With Your Invoice/ Billing Software?
FAQ’s
-
What is NRT GST registration for ISDs?
- NRT GST registration for ISDs refers to the process of registering as an Input Service Distributor (ISD) for Non-Resident Taxpayers (NRT) under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) system.
-
What are the eligibility criteria for NRT registration as an ISD?
- To register as an ISD, NRTs must meet criteria such as being liable to pay GST, providing eligible services, and being non-resident entities without a physical presence in India.
-
What are the special requirements and procedures for NRT ISD registration?
- Special requirements may include appointing a local representative, providing additional documentation to confirm non-resident status, and following specific procedures outlined by the GST authorities.
-
Tax implications and compliance obligations for NRT ISDs
- NRT ISDs are liable to pay GST on services provided in India and can claim input tax credits for GST paid on eligible inputs. Compliance obligations include filing returns and maintaining proper records.
-
Role of NRT ISDs in the GST supply chain
- NRT ISDs facilitate the distribution of input tax credits among different branches or units of a company, ensuring fair allocation and efficient utilization of resources within the organization.
-
Managing NRT ISD registration and compliance effectively
- Effective management involves understanding regulatory requirements, appointing a local representative, maintaining thorough documentation, and utilizing technology for streamlined compliance processes.
-
Can a non-resident entity register as an ISD if it doesn’t have a physical presence in India?
- Yes, non-resident entities can register as ISDs under GST even if they don’t have a physical presence in India, provided they meet the eligibility criteria and fulfill all necessary requirements.
-
Are there any specific procedures for NRT ISD registration different from resident entities?
- Yes, NRT ISDs may need to follow additional procedures such as obtaining clearance from relevant authorities and providing proof of non-resident status during the registration process.
-
What happens if NRT ISDs fail to comply with GST regulations?
- Non-compliance with GST regulations by NRT ISDs may result in penalties or other enforcement actions by the tax authorities, highlighting the importance of maintaining compliance.
-
Can NRT ISDs distribute input tax credits to branches outside India?
- No, input tax credits can only be distributed among branches or units within India. NRT ISDs cannot distribute credits to branches located outside the country.
