Introduction to Goods and Services Tax (GST)
The Goods and Services Tax, commonly known as the GST, established the groundwork for an extensive overhaul of India’s tax structure. Since its implementation in 2017, the GST taxation system took the place of other indirect taxes imposed on various goods and services as a result of this tax reform. GST is a comprehensive tax imposed at every value-addition stage and the tax is applied to products and services sold for consumption inside India’s national borders. As a result, the GST compliance benefits are many and has helped to streamline India’s indirect tax system. In this article, we will discuss the topics that will clarify all your inquiries regarding the benefits of the GST system.The Importance of GST Compliance
The advantage of a single tax is that it ensures that the cost of a certain commodity or service is the same in every state. That is the reason why the importance of GST compliance cannot be overstated. It is necessary to adopt certain common laws, such as e-way bills for the transportation of products and e-invoicing for transaction reporting, to implement GST compliance. Tax compliance has also been enhanced since taxpayers are not burdened by several return forms and deadlines.1. Controls Indirect Taxes
At many points in the supply chain, India used to apply indirect taxes such as service tax, central excise, VAT, and other taxes. While the states oversaw certain taxes, the federal government oversaw others, but there was no centralized tax on goods and services, and then the GST was put into place. Under the GST, the primary indirect taxes were merged into one, and the government’s administration of tax compliance rules and taxpayers’ burden have been greatly reduced as a result.2. Protection against Tax Evasion
Compared to earlier tax rules, the GST is far more stringent because taxpayers now only claim an input tax credit on invoices filed by each of their suppliers. This reduces the likelihood of fraudulent invoices being able to claim input tax credits, and the introduction of electronic invoicing has enhanced this objective even further. One of the main GST compliance challenges was tax fraud, but now the new system has greatly improved the effectiveness of the crackdown on noncompliant persons. The below chart shows the types of GST and how those taxes are implemented.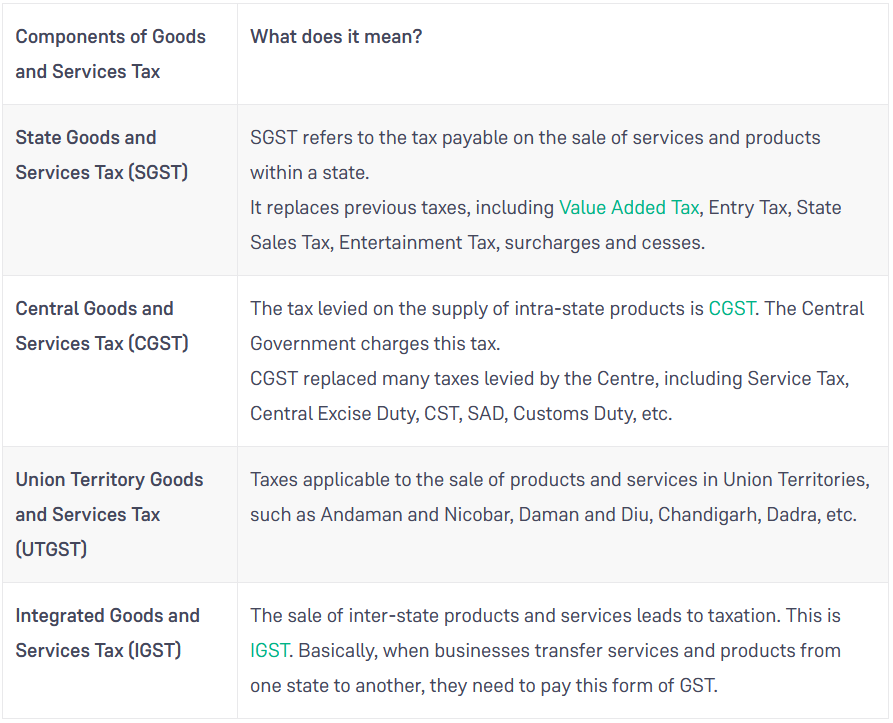 Also Read: Different Types of Documentation Required for GST Compliance
Also Read: Different Types of Documentation Required for GST Compliance
Streamlining Operations Through GST Compliance
All GST-related processes can be completed online, including GST registration and GSTR filing. This system helps streamline operations and increases compliance among taxpayers.- The tax-paying process has been considerably simplified, making it easier for people to complete their GST-related services in one place.
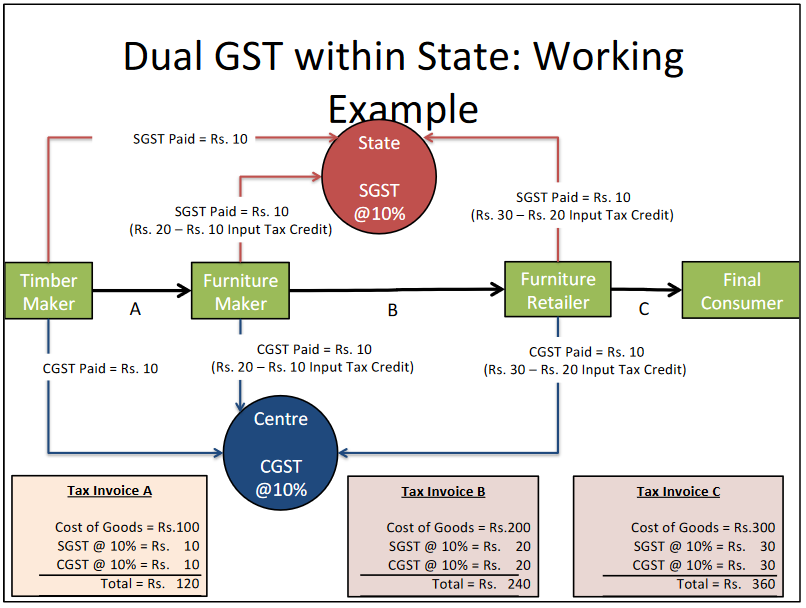
- The two halves of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) are Central GST (CGST) and State GST (SGST), and GST is imposed concurrently throughout the value chain by the Centre and the States.
- Every supply of goods and services above a certain sum is subjected to GST tax. On all transactions within a State, the State Goods and Services Tax (SGST) would be levied and collected by the States, while the Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST) would be collected by the Central Government.
- Every transaction involving the provision of goods and services will be subject to both the Central GST and the State GST, except for those that are exempted, fall outside the ambit of the GST, or are conducted below the designated threshold limitations.
- Unlike State VAT, which is imposed on the value of the items plus Central Excise, both Central GST and State GST would be levied on the same price or value.
Financial Implications and Benefits of GST
Since the implementation of the GST Act, the financial implications of the system have affected every industry. The impact of GST on businesses cannot be overstated as the new act provided many benefits.1. Competitive Pricing Boosts Consumption Levels
The adoption of the GST has resulted in a rise in consumption and indirect tax revenues. Due to the former tax regime’s cascading taxation, the final price of any goods became quite high. Prices are now more competitive both locally and abroad thanks to stable GST rates. As a result of more fair pricing, demand has also increased.2. Efficient Distribution and Logistics
Among its numerous benefits, GST promotes warehouse consolidation, improves supply chains and turnaround times, and shortens transportation cycle times. Under a single indirect tax system, the delivery of products does not require much paperwork. Because of the e-way bill system under the GST, the industry gains the most in terms of passage and arrival efficiency from the removal of interstate checkpoints, and that lowers the high expenses related to logistics and warehousing.3. Online System Helps Businesses Operate Quickly
In the past, taxpayers had a great deal of trouble communicating with different tax authorities under each tax law. Furthermore, even though returns were filed online, the majority of the evaluation and reimbursement procedures were carried out offline. Almost all GST processes are now done online, including registration, return filing, refunds, and the creation of e-way bills. This has made it easier to conduct business and substantially streamlined taxpayer compliance.4. Uniformity of Tax Rates
By guaranteeing uniform indirect tax rates throughout the nation, the Goods and Services Tax (GST) improves predictability and facilitates corporate operations. Put otherwise, the GST provides uniformity when people conduct business, and the location of the business owner does not affect tax rates.5. Elimination of the Tax Cascading Effect
There is less tax cascading with GST because now a system is in place that works across state lines and throughout the value chain. This has lowered ongoing operating expenses as GST has taken the role of other indirect taxes at the federal and state levels. With the support of a strong end-to-end IT infrastructure, the GST is less complicated and easier to manage than any previous indirect taxes imposed by the State and the federal government. Also Read: Benefits Of GST RegistrationEnsuring Regulatory Compliance: Strategies and Best Practices
GST is a multi-stage and comprehensive tax that is a replacement for several indirect taxes across the nation. The tax is applied to products and services that are sold for consumption inside India’s national borders. The government has put various GST compliance strategies in place so that the rules of the GST act are not misused for personal gains and fraudulent activities are stopped by the authorities.- The maximum retail price is reflected by applying GST to the final market price of products and services that are internally manufactured.
- When purchasing products or services, customers must pay this tax, because it is included in the final cost.
- Across the nation, the GST rates on various goods and services are applied consistently. Nonetheless, different tax slab rates have been applied to different categories of goods and services.
- Necessary products have been placed in lower and zero slab rates, while comfort and luxury products are classed under higher slab rates. This classification’s primary goal is to guarantee that citizens receive an equitable distribution of wealth.
| 5 percent | Essential goods, food items, life-saving drugs, etc. |
| 12 percent | Apparel items, packaged food, medicines, etc. |
| 18 percent | Electronic items and most services |
| 28 percent | Luxury goods, cars, tobacco, drinks, etc. |
Conclusion
The goods and services tax (GST) is imposed on the majority of products and services that are sold for domestic use. Although customers pay the GST, the companies that sell the products and services are the ones that send it to the government. However, GST may disproportionately affect those whose income is in the lowest levels. To solve these issues, the government has implemented GST-exempt products and lowered GST rates on food and life-saving drugs. To lessen the burden of GST on small businesses, the government also provides an income limit below which paying GST is not necessary. However, all businesses must follow the GST compliance rules because the GST system can provide uniformity and much needed structure in the tax system.FAQs
-
What are the main objectives of GST?
-
What are the three components of GST?
-
How does the GST system work for the manufacturers and retailers?
-
What are GST registration and GST returns?
-
Who is eligible for paying GST?
-
How are imported products taxed under GST?
-
Are the VAT and the GST the same system?
-
What are the features of the GST returns filing procedures?
-
What are the logistics and distribution systems under GST?
-
Does GST promote competitive pricing and increase consumption?
Maximize your business potential by embracing GST compliance effectively.
Ahana Das
Freelancer
Ahana is an accomplished writer who has covered her graduation in English Honours. Having written in various subjects, she takes particular interest in writing content on personal finance, investing, budgeting and financial planning and her articles on finance and current affairs are seldom published in global newspapers.
