To track the transportation of products and avoid tax cheating, the government has implemented the concept of e-way bills. When a person with GST registration moves items worth more than INR 50,000, he or she must generate an e-way bill. However, in some cases, e-way bill creation is not required.
How does the e-way bill mechanism work?
Everyone who is subject to e-way bill compliance must first register on the shared site. They can then generate the e-way bill. When the e-way bill is generated on the common portal, a unique e-way bill number will be made available to all three parties on the common portal, i.e.
- The supplier
- The recipient
- The Transporter
Following the submission of Part A of form GST EWB-01, the other party can view the e-way bill generated against his/her GSTIN via the common portal.
The opposite party is now compelled to accept or reject the consignment described in the e-way bill. Please keep in mind that if the acceptance or rejection is not expressed within 72 hours after the generation of the e-way bill or the delivery of goods, whichever comes first, it will be assumed that he has accepted the terms.
Also Read: How Does an E-Waybill Work?
What Are the Different Requirement Cases for an E-Way Bill?
The following situations necessitate the use of an e-way bill:
- Goods are carried from one state to another with a value greater than ₹50000 (except in some areas where the threshold is lower).
- A person registered as a consignor or recipient is transporting items in someone else’s vehicle.
- Supplying entails the transfer of items via an e-commerce operator or a courier service.
- A primary is moving items to or from a job worker.
- When an unregistered individual sells products to a registered person for more than ₹50000.
Documents to have on board if a e-way bill is not necessary
An e-way bill will be a valuable tool for detecting tax evasion at multiple locations and tracking the transit of products. When an e-way bill is not required, the transporter must guarantee that a copy of the tax invoice or a bill of supply is carried.
An example demonstrates how the e-way bill might be used to avoid paying taxes. If raw materials are carried from Karnataka to Tamil Nadu, where they are processed and sold, the state from which they should get revenue is Tamil Nadu because it is the state of consumption.
However, if half of the finished goods are moved to another state, say Kerala, and then sold there, Kerala receives the revenue share.
The e-way bill is helpful in this situation. It allows us to precisely understand the movement of products in each state, which aids in preventing tax evasion.
As a result, the e-way bill is an important document that facilitates the transportation of products from one location to another.
An e-way bill can be prepared online by uploading necessary details such as the type of products, the HSN code, the quantity and taxable value, the recipient’s details, the transporter’s details, the vehicle number, etc. Before the movement of goods can begin, the taxpayer/transporter must generate an e-way bill.
As a result, it goes without saying that if statutory provisions cover a taxpayer, the items should always be covered by an e-way bill. If not, he must carry a copy of a tax invoice or the valid document specified under the GST Invoicing regulations.
What Documents Are Required for E-Way Bill Exemption?
In circumstances where an E-Way Bill is not required, you must carry the following documents:
- Invoice
- Bill of supply or bill of entry
- Delivery challan
- ID proof for the transporter, such as a PAN card, Aadhaar card, etc.
- Copy of E-Way Bill or E-Way Bill number
- E-Way Bills mapped to RFID
Specific goods exempted from e-way bill
Transportation of the commodities stated in the annexure to the rules as follows:
- Liquefied petroleum gas for supply to exempted household and non-domestic clients
- Kerosene oil is distributed through the Public Distribution System (PDS).
- The Department of Posts transports postal baggage.
- Natural or cultured pearls, valuable or semi-precious stones; precious metals and precious metal clad metals
- Jewellery, goldsmith and silversmith products, and other items
- Currency
- Personal and home effects were employed.
- Coral, both unworked and worked.
Transported goods include alcoholic beverages for human consumption, petroleum crude, high-speed diesel, gasoline, natural gas, and aviation turbine fuel.
Goods in transit are not considered supplies under Schedule III of the Act. Schedule III includes actions that are neither a supply of commodities nor a service, such as service by an employee to an employer in the course of his employment, functions performed by MPs and MLAs, and so on.
The shipping of goods other than de-oiled cake is defined in Notification No. 2/2017-Central Tax (Rate) dated June 28, 2017. The following are some of the items listed in the aforesaid notification:
- Buttermilk, lassi, and curd
- Fresh milk and pasteurized milk that do not have added sugar or other sweeteners
- Vegetables and fruits
- Tea leaves and coffee beans that have not been processed
- Animals, plants, and trees that are alive
- Cereals with Meat
- Rice and wheat flour that are not branded
- Salt
- Books, maps, and periodicals of instructional value
Goods exempted under Notification No. 7/2017- Central Tax (Rate) dated June 28, 2017 (supply by CSD to unit-run canteens and permitted consumers) and Notification No. 26/2017- Central Tax (Rate) dated September 21, 2017 (heavy water and nuclear fuels).
Specific transactions that do not necessitate the use of a e-way bill
Other transactions in which an e-way bill is not necessary include:
- For goods worth less than Rs. 50,000, an e-Way Bill is optional (unless in circumstances where mandatory e-way bill rules apply, such as the transfer of handicraft goods and goods for interstate job work).
- If items are conveyed by a non-motorized conveyance (for example, horse carts or manual carts),
- If commodities are being moved:
- Customs clearance from the port, airport, air cargo complex, and land customs station to an inland container depot (ICD) or container freight station (CFS).
- Under customs bond, from an ICD or CFS to a customs port, airport, air cargo, etc.
- Under customs bond, from one customs port/station to another.
- Goods transported under customs control or bearing a customs seal
- Transported goods inside the specified area
- Goods are carried from/to Nepal/Bhutan.
- If products are transported within 20 kilometers of a weighbridge and returned to the establishment of business covered by a Delivery (DC) Challan
- When the government or a municipal government transports goods by rail as a consignor,
- Goods transport to and from the Ministry of Defence
As a result, if a taxpayer falls under any of the categories listed above, he will not be required to generate an e-way bill. Though taxpayers who qualify for e-way bill exemptions are excluded from this requirement, they must still verify that other documents, such as the invoice and bill of supply, comply with the rules and regulations. A taxpayer who violates the e-way bill rules faces severe penalties.
No late fee for GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B returns
The 31st GST Council’s most significant concession to small businesses is the elimination of the late fee for filing GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B returns. The GST Council has made the following announcements:
“Late fee shall be completely waived for all taxpayers in case FORM GSTR-1, FORM GSTR-3B &FORM GSTR-4 for the months/quarters July 2017 to September 2018, are furnished after 22.12.2018 but on or before 31.03.2019.”
Thus, completing Form GSTR-1, GSTR-3B, and GSTR-4 will not result in a late fee penalty until March 31, 2019.
GST Annual Return Due Date Extended
All firms with a GST registration must file a GST annual return in form GSTR-9. The GST yearly return is usually due on December 31 of each year for the fiscal year that concluded on March 31 of the same calendar year. Because GST is new in India, the government has decided to extend the deadline for filing GST annual returns to June 30, 2019. The deadline for filing the GST annual return was initially developed to March 31, 2019, but the GST Council has now extended it to June 30, 2019.
What are the advantages of e-way bill?
There are various advantages to using the e-way bill mechanism. It is going to:
- Allow for speedier movement of goods.
- Improve truck turnaround time now that the checkpoint has been removed. As a result, the logistics industry will profit by cutting travel time and expense while increasing the distance traveled.
- E-way bill generation technology that is simple to use. This means that there is no need to contact the e-way bill department to generate an e-way bill, which was a considerable inconvenience in the previous system. The e-way bill can be generated straight online.
- Because the entire system is online, tax evasion is avoided.
Also Read: What are the Benefits Of Using an e-way Bill?
Which form needs to be filled out for the generation of the e-way bill, and by whom?
Form GST EWB-01 can be used to generate an e-way bill when items are transported by truck.
- The registered person as a consigner or the recipient of the supply as the consignee,
- by whatever mode–in his own conveyance or a hired one, or by rails, air, or sea.
Form GST EWB-01: Part A and Part B
- Part A of Form GST EWB-01 includes information about invoices, suppliers, receivers, and invoice items with HSN codes and tax rates.
- Part B of Form GST EWB-01 includes transporter information such as manner of transfer, approximate kilometers, Name, Transporter ID, date, and vehicle number.
Please keep in mind that an e-way bill will only be considered generated if the information in Part B of form GST EWB-01 has been submitted.
Because there are several parties involved, we have outlined who is necessary to fill out which section of Form GST EWB-01 to minimize confusion:
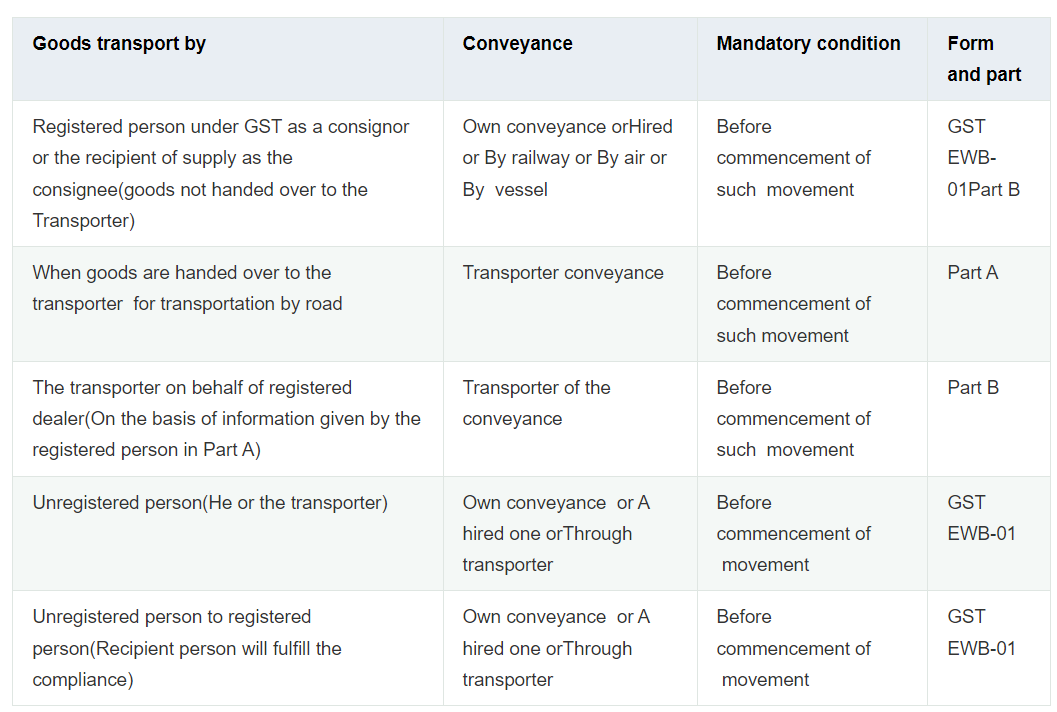
Also Read: Who Is Required To Generate An E-Way Bill?
Wrapping It Up
Certain types of commodities are excused when an E-Way Bill is not necessary to make compliance easier for taxpayers. Other papers, such as invoices and bills of supplies, should, however, still be in line with the norms and regulations. Failure to follow E-Way Bill standards can have severe ramifications and penalties for taxpayers.
FAQs
-
When will the e-way law be made mandatory?
The preparation of an e-way bill is optional if the value of the products being transported is less than Rs. 50,000. If the supplier is not GST-registered, but the recipient is, an E-way bill is also required.
-
What is the e-way bill distance exemption?
There is no need for an e-Way bill for the transportation of goods up to a distance of 20 kilometers from the consignor’s place of business to a weighbridge for weighing or from the weighbridge back to the consignor’s place of business.
-
Is it possible to produce an e-way bill without a vehicle number?
When generating part A of the e-Way bill, the Vehicle Number entry is optional. However, an e-Way Bill without a vehicle number is ineffective for the movement of goods.
-
What is the deadline for submitting an e-waybill?
To compute the validity, for every 200 kilometers traveled, one day is added to the validity period.
-
Can we produce a new e-way bill after the expiry date?
The validity time of an e-way bill can be extended. This option is available for developing the validity of an e-way bill before and after 8 hours.
-
What are the most recent modifications to the e-way bill?
Following that, the government expanded the application of e-invoicing to firms having a turnover of more than Rs 20 crore as of April 1, 2022.
-
Why is alcohol excluded from GST?
To ensure that state governments have a reliable source of revenue other than GST.
-
In what circumstances is an e-way bill not required?
When the value of the products transported is less than $50000, you do not need to generate an E-Way Bill.
-
What is the GST waybill distance limit?
The lowest distance required for an e-way bill is 50 kilometers, and the maximum e-way distance limit is 4,000 kilometers.
-
Is it possible to sell my gold ring without a bill?
A genuine gold buyer will always request the original purchase bill when purchasing gold from you.