Introduction to GST Audit
The Goods and Services Tax, commonly known as GST, has fundamentally altered the structure of the Indian tax system. It not only simplified the nation’s indirect tax system, but also made it easier for companies to abide by tax regulations. However, the implementation of GST necessitates the requirement for a GST audit process, which is the process of demonstrating the accuracy of GST returns that a taxpayer files.
Businesses that generate more than Rs 5 crores in revenue annually are required to undergo this GST audit. It is carried out by a qualified chartered accountant who verifies that the taxpayer’s GST returns are correct and compliant with the applicable legislation. Identifying the tax return mistakes, inconsistencies, and non-compliance problems is another aspect of this process, and these problems can be rooted out by a GST audit.
To guarantee GST compliance and reduce the possibility of penalties and fines, GST audits are crucial for companies in every industry. GST audits also improve the business’s reputation and aid in improved risk management. You may focus on growing your business and feel secure knowing that you are in compliance with the law by leaving your tax management to GST audit consultants.
In this article, we will provide a thorough review of the GST audit process and discuss the following topics:
- Preparing for a GST Audit
- The GST Audit Process
- Key Aspects of a Comprehensive GST Audit
- Benefits of a Comprehensive GST Audit
- Best Practices for a Successful GST Audit
Also Read: Audit And Documentation Requirements For GSTR-10
Preparing for a GST Audit
For a GST audit, a comprehensive review of financial records, tax returns, and other documents must be done, and those documents have to be provided by the taxable person. The auditor’s purpose is to verify the accuracy of turnover declared, taxes paid, refunds claimed, and input tax credits availed, as well as to assess the taxable person’s compliance with the provisions of this Act.
If you are preparing for a GST audit, make sure that the following paperwork is gathered and everything is in order.
- Annual returns get filed under the Goods and Service Tax Identification Number.
- GSTR 9 is utilized to receive the Reconciliation Statement Certificate.
- The Reconciliation Statement Certificate must match the value of the supply, tax, and the stated amount in Form GSTR 9 with the audited financial reports.
- Copies of the balance statements and profit and loss statements of your business.
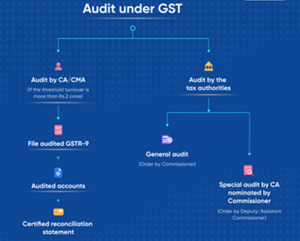
The GST Audit Process
Understanding the fundamentals of the GST audit process and the GST compliance checklist is necessary before the comprehensive GST audit process starts. It is also essential to comprehend how to acquire a Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for the GST audit and learn about the types of GST audits.
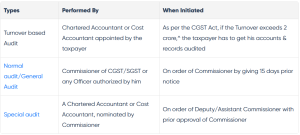
1. Turnover Based Audit
This kind of GST audit happens when the taxpayer’s total revenue surpasses two crore Indian rupees, and in these cases, an appointment of a CA is required to lawfully complete the audit.
2. General Audit
This kind of GST audit occurs when the GST Commissioner passes an order, but the taxpayer is given at least 15 days’ notice before the audit process begins. The CGST/SGST Commissioner or any other individual designated by the GST Commissioner has the power to conduct a general audit.
3. Special Audit
This kind of GST audit is used when the deputy or assistant commissioner passes an audit order, however, these officials must first obtain the GST Commissioner’s consent. They must also create a GST internal audit checklist before they can begin the audit process. The GST commissioner may designate a CA or CWA as needed to carry out a particular special audit.
The below chart shows how these three types of audits are performed and when they can be initiated.
Key Aspects of a Comprehensive GST Audit
The GST audit process is done by the book, and the auditors must follow all the steps mentioned below to comply with the audit laws:
- At least 15 working days before the audit is conducted, the taxpayer is formally informed of the impending audit. The taxpayers receive the FORM GST ADT-01 and are made aware of the impending audit.
- FORM GST ADT-01 also identifies the data and documents that must be supplied to the auditor for a preliminary assessment. There is a 15-day window within which the taxpayer must submit the paperwork.
- When the auditor approves the documentation that the taxpayer has supplied, he/she starts the process of verifying the company records, and the audit will formally begin.
- The authorized officer may ask for access to various documents during the audit in order to confirm the accounts or other financial details provided by the taxpayer are correct.
- The verification of audits can take place in the designated officer’s personal office or the taxpayer’s place of business.
The auditee, or taxpayer, receives the preliminary results upon completion of the audit verification and within 30 days of the observations being finalized, the auditee/taxpayer receives the results in the form of a Final Audit Report (Form GST ADT-02). The entire audit process must be finished in full within three months of the start date, with an additional six months allowed if needed.
Benefits of a Comprehensive GST Audit
A GST audit is a crucial process for confirming compliance and assessing a taxpayer’s degree of conformity with the requirements of the CGST Act rules. The tax-compliant auditee can receive many advantages by following all the GST audit requirements.
- The foundation of the whole GST system is the GST taxpayer’s self-assessment and self-compliance, and its goals are to increase openness, discourage tax evasion, and direct companies toward accurate compliance.
- As taxpayers become more knowledgeable about tax rules and processes, compliance rules become easy to follow.
- Taxpayers’ self-assessments and GST returns are produced precisely, with a greater emphasis on accuracy and completeness.
- Taxpayers may identify and fix flaws in their internal control and accounting systems with the use of GST audits.
- A thorough GST audit reduces unwanted hassles for the taxpayer because these audits considerably reduced the likelihood of legal actions.
Best Practices for a Successful GST Audit
The auditor is in charge of following the GST audit checklist and looking through balances, ledgers, invoices, annual financial accounts, and other audit reports to find non-compliance, and revenue leakage.
- The primary duty of the auditor is to reconcile the annual return (GSTR 9, GSTR 9B) and the audited financial statements of the company.
- Form GSTR 9C must be analyzed by auditors using their professional judgment, expertise, and understanding of the GST audit rules.
- The auditor must determine if the business is correctly managing its accounts in the ERP system and whether the business’s accounting system maintenance process is dependable.
- An auditor must assess the internal system of the business to see whether a thorough audit is required and may ask for documents to learn more about a company’s operational procedures.
- The auditor may have conversations with the business owner when conducting the audit and must keep a thorough written log of all the things he/she observes about the internal control system of the company.
- The auditor must decide if the taxpayer needs to pay any due taxes and is required to report any revenue leaks that might lead to underpayment or nonpayment of taxes owed.
- The auditor’s scope is limited to reconciling the turnover recorded in GST returns and financial statements, as well as reporting any extra liabilities that may result from non-reconciliation.
- It is not necessary for the auditor to assume the position of an investigator in order to identify supplies that are not declared and aren’t included in the financial statements or the annual report. Only the mistakes or omissions that the auditor discovered during the audit, in accordance with auditing standards, are required to be disclosed.
Conclusion
The process of reviewing a company’s financial records, returns, and other paperwork kept by the taxable person is known as an audit under GST. Verifying the accuracy of turnover reported, taxes paid, refunds requested, input tax credit claimed, and compliance with GST regulations are the main goals of these types of audits. Additionally, a GST audit verifies that all turnover declarations, taxes paid, refunds requested, input tax credits obtained, and other compliances with the GST Act are accurate and examined by a qualified specialist.
A taxpayer under the goods and services tax (GST) must determine their tax amount, pay the taxes, and file the necessary reports. GST is a trust-based system, but sometimes a strong audit process is essential to verify if the person has accurately self-assessed the taxes that the company must pay. The government is taking several actions to ensure that the GST is implemented correctly and people are following compliance rules, and that is why the government is using the GST audit system.
Also Read: GST Audit: When And How GST Audits Are Conducted And What Businesses Need To Prepare
FAQs
-
What is a GST audit?
An audit is the process of checking the financial records, returns, and other paperwork of a company that the registered taxpayer has provided to the government. This process is done to confirm that the turnover, taxes, refunds, and input tax credit that the taxpayer has claimed as accurate are correct and they comply with the terms of the CGST Act.
The legal foundation of GST audit is found in Section 65(1) of the Central Goods and Service Taxes Act, 2017, which states that any registered person may be the subject of an audit by the general or special order of the Commissioner or any other officer designated by the Commissioner. The duration and method of the GST audit process are also specified by the Commissioner or the designated officer.
-
What is the process of a GST Audit?
The GST audit is the process of checking the documents provided by a taxpayer that are used to maintain the books of account and the returns and statements of the company. The taxpayer must provide these details in accordance with the Act, and the details must be verified by an auditor assisted by a team of officers and officials from the department authorized to conduct an audit of the registered person’s records and books of account. The team will confirm the accuracy of the turnover, claimed refunds, claimed exemptions and deductions, the rate of tax applied to the supply of products or services, the input tax credit claimed and used, and other pertinent matters, noting the findings in the audit notes.
-
What is a special audit, and who can order it?
A special audit may be started if, at any point during the audit examination, investigation, or inquiry, the auditor believes that the financial value has not been accurately stated or incorrect credit has been obtained by the taxpayer. Taking into account the complexity and character of the case as well as the interest of income, the Assistant Commissioner may start the special audit. Even in cases when the taxpayer’s books have already undergone an audit, a special audit may nevertheless be carried out. The Assistant Commissioner may request a special audit from the Commissioner, and with the Commissioner’s consent, a chartered accountant or a cost accountant chosen by the Commissioner will conduct the special audit.
-
How are the special audit results dealt with?
The taxable person will have a chance to comment on the special audit’s conclusions, but demand and recovery proceedings will get started if the audit finds unpaid or underpaid taxes, incorrect refunds, or incorrectly claimed input tax credits. The report must be turned in by the auditor within ninety days, however, through a request from the auditor or the taxable person, the tax officer may further extend this process for an additional ninety days. The Commissioner shall decide on the matter and cover the costs associated with the audit and examination, including the auditor’s compensation.
-
What are the principles of a GST Audit?
The selection of taxpayers to be audited is based on the risk factor of tax evasion, and this is the first step in the audit process. The main goal of a GST audit is to ensure efficiency by converting the identified risk indicators into a relevant review and an audit plan. An effective audit is ensured by the commissioner by outlining a systematic and comprehensive approach that will get followed by the GST audit officials. Depending on the determined type of risk factors, an auditor’s degree of examination and application can vary, and the time length for the audit is made flexible for that reason. GST laws state that the entire audit, including all checks and conclusions, should be well documented by the auditor at all points so that other people can determine the unknown parameters for compliance verification.
-
What are the GST audit rules?
At least fifteen days before the GST audit procedure, the auditee must receive a formal notification that states that the GST audit process will get started by the authorities. The GST audit procedure begins once the auditee provides the necessary paperwork to the auditor within the time limit and the auditor accepts it, or after the company premises are verified. The authorized officer may see and confirm the required documents during the audit. Following completion, preliminary results get sent to the auditee, and the Final Audit Report (Form GST ADT-02) is released thirty days later, and the auditee may settle any tax disparities. The goal of the GST audit procedure is to finish it in three months, with a six-month extension option, and trade facilitation and a non-intrusive environment for taxpayers are given top priority during the GST audit procedure.
-
Is a GST audit necessary?
Certain GST taxpayers require a GST audit because, during the GST audit, the company’s records, returns, and other financial papers are reviewed by the auditor for discrepancies. It aims to ensure that the recorded turnover is correct and that all GST taxes are paid for the fiscal year by the taxpayer. An audit expert is designated and authorized by the GST commissioner to oversee, verify, and perform the audit as required by the GST Act.
-
What is the applicability and turnover limit of a GST audit?
Every registered taxpayer whose total revenue during a financial year exceeds Rs. five crore can be required to undergo an audit of his accounts, per sub-section (5) of section 35 of the CGST Act. If the turnover of the registered person exceeds INR five crore in a fiscal year, a statement properly attested in Form GSTR-9C must be filed by the taxpayer. The mandatory GSTR 9 filing threshold is set at Rs. two crore, whilst the GSTR 9C threshold is set at Rs. five crore, and Form GSTR-9 filing is not required for GST-registered taxpayers whose annual aggregate income does not exceed Rs. two crore.
-
What are the penalties that can result from a GST audit?
To unify India’s markets and streamline the intricate network of State and Central Taxation Laws, the Goods and Services Tax (GST) was implemented in the year 2017. Concerning taxable events, tax rates, points of levy, return filing, tax payment, refunds, audits, appeals, and other aspects, consistency was ensured by the Goods and Services Tax (GST). The GST Act does not outline any consequences for non-compliance, but it specifies that the annual return and audit deadlines, and a general penalty of Rs. 25,000 will apply if the paperwork is not filed within the time limit.
-
How long is the GST audit process?
The audit process is usually done within fifteen days if the taxpayer submits all the necessary documents within that time frame. However, if further paperwork is needed for any kind of examination, the timeframe could be extended by the authorities. The number of days may be raised proportionately, with an increase of 25% of working days for each extra year of coverage, if the audit coverage is for five years. The general rule is that the audit must be finished within three months from the day the audit was started. If the Commissioner determines that an audit on a taxpayer cannot be finished in three months, he may choose to extend the deadline by an additional period of time that cannot exceed six months.