In the realm of modern logistics and transportation, E-waybills stand as a critical instrument facilitating the seamless movement of goods across and within regions. However, the management of expired E-waybills poses a significant challenge for businesses engaged in the transportation of goods.
Addressing this issue effectively necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the procedures and documentation requirements involved.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of managing expired E-waybills, exploring the essential steps and documentation protocols essential for businesses to navigate this aspect of the logistics landscape efficiently.
Expired E-waybill Management Procedures
Expired E-waybills can pose challenges during transportation. Here’s a general procedure to manage them:
| Identify the Expiry | Check the expiration date on the E-waybill to ascertain its validity. |
| Renewal or Generation | If the E-waybill has expired before the completion of the journey, generate a new E-waybill to continue the transportation legally. |
| Document Retention | Keep records of the expired E-waybill and the new one generated for auditing purposes. |
| Communication | Inform relevant authorities or stakeholders about the expired E-waybill and the subsequent generation of a new one to maintain transparency. |
| Compliance Check | Ensure compliance with local regulations regarding expired E-waybills. Some regions might have specific procedures to follow. |
| Penalties and Fines | Be aware of any penalties or fines associated with expired E-waybills. Take necessary actions to rectify the situation to avoid additional charges. |
| Review Procedures | After addressing the immediate issue, review internal procedures to prevent such occurrences in the future. Implement systems to track and manage E-waybill expirations effectively. |
Remember, managing expired E-waybills promptly is crucial to avoid disruptions in transportation and potential legal issues.
Documentation requirements for expired E-waybills
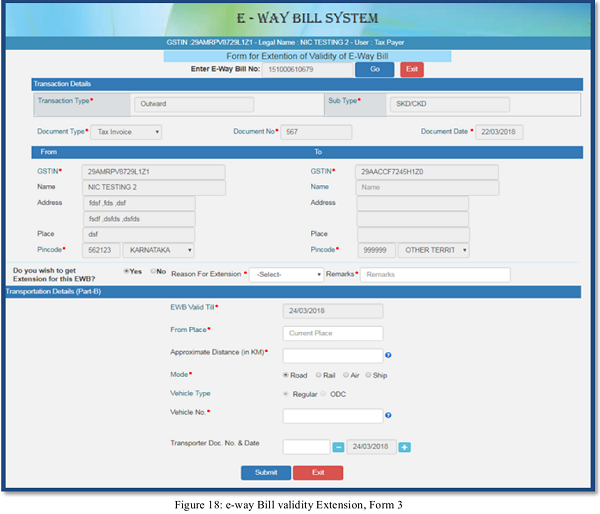
When dealing with expired E-waybills, it’s important to manage the documentation properly to maintain compliance:
| Record Keeping | Maintain a record of the expired E-waybill, noting its unique identifier, expiry date, and details of the transportation it pertained to. |
| New E-waybill Generation | Document the generation of a new E-waybill to continue the transportation after the expiry of the original one. Keep a copy of the renewed E-waybill. |
| Timestamps and Dates | Clearly mark the dates of expiration and renewal of the E-waybill on your records for future reference and auditing purposes. |
| Communication Logs: | Keep a log of any communications made with relevant authorities or stakeholders regarding the expired E-waybill and its subsequent renewal. |
| Compliance Verification | Ensure that the new E-waybill complies with all necessary regulations and contains accurate information regarding the shipment |
| Retention Period: | Follow the prescribed retention period for these documents as per local regulations. Typically, this is for a specified period after the completion of the transportation or as mandated by authorities. |
| Auditing and Review | Periodically review your documentation procedures to ensure they align with any updates in regulations or best practices. This helps in maintaining a streamlined process for managing expired E-waybills |
By maintaining comprehensive documentation, you can ensure transparency and compliance with regulations, aiding in smooth operations and mitigating potential issues during transportation.
Legal provisions for handling expired E-waybills
The handling of expired E-waybills is subject to legal provisions that vary by jurisdiction. Some common legal considerations include:
- Renewal Procedures: Many regions have provisions allowing for the renewal or extension of E-waybills that have expired during transit. Check local regulations for specific procedures regarding renewal.
- Penalties and Consequences: Legal frameworks often outline penalties or consequences for using expired E-waybills. This can include fines, penalties on the transporter, or potential delays in transportation until a valid E-waybill is obtained.
- Reporting Requirements: Some jurisdictions mandate reporting the use of expired E-waybills to relevant authorities within a specified timeframe. Failure to report or rectify the situation could result in penalties.
- Auditing and Compliance: Legal provisions may necessitate the maintenance of records for a designated period, allowing authorities to audit E-waybill usage and compliance. Non-compliance might lead to legal repercussions.
- Exceptions and Exemptions: Certain situations might be exempted from stringent penalties, such as cases where immediate renewal is not possible due to unforeseen circumstances. Check for provisions allowing exceptions in such cases.
- Appeals and Dispute Resolution: Legal frameworks often provide procedures for appealing penalties or disputing issues related to expired E-waybills. Understanding these procedures can be crucial in resolving disputes.
It’s crucial to thoroughly understand the legal provisions specific to your region regarding expired E-waybills to ensure compliance and take appropriate actions in managing and rectifying expired E-waybill situations. Consulting legal experts or relevant authorities for precise guidance is advisable.
Compliance obligations for managing E-waybill expiry
Managing E-waybill expiry comes with several compliance obligations to ensure adherence to regulations:
- Timely Renewal: Renew expired E-waybills promptly to avoid legal issues. Compliance often demands the generation of a new E-waybill after the expiry to continue transportation legally.
- Accurate Information: Ensure that the renewed E-waybill contains accurate and updated information about the shipment, reflecting any changes from the expired E-waybill.
- Documentation Retention: Maintain records of both the expired and renewed E-waybills. Compliance often requires preserving these documents for a specific period for auditing purposes.
- Reporting and Notifications: Some regulations mandate reporting the use of expired E-waybills to relevant authorities within specified timeframes. Notifications about the renewal might also be necessary.
- Penalties and Fines: Compliance obligations usually outline penalties or fines for using expired E-waybills. It’s crucial to understand these consequences and take necessary actions to avoid them.
- Audits and Inspections: Be prepared for audits or inspections by regulatory bodies. Compliance often involves having proper documentation and processes in place to manage E-waybill expirations.
- Adherence to Regulations: Ensure overall compliance with all regulations concerning E-waybills, including any specific provisions related to their expiry and renewal.
Meeting these compliance obligations helps in maintaining legality and transparency in transportation operations while avoiding potential fines or legal issues stemming from expired E-waybills.
Reporting requirements for expired E-waybills
Reporting requirements for expired E-waybills are critical to maintaining compliance and transparency in transportation operations. When an E-waybill expires, it’s imperative to report this occurrence accurately and promptly to the relevant authorities or governing bodies as per regulations.
Typically, this involves documenting the expired E-waybill details, reasons for expiration, and any necessary corrective actions taken. Timely reporting ensures regulatory compliance and helps prevent potential penalties or disruptions in the transportation process.
Challenges in managing expired E-waybills
Managing expired E-waybills presents several challenges within the logistics landscape. Some of these hurdles include:
- Compliance Issues: Keeping track of numerous E-waybills and their expiration dates across various shipments can lead to inadvertent lapses in compliance.
- Operational Disruptions: An expired E-waybill can disrupt the transportation process, causing delays and potentially impacting delivery schedules.
- Administrative Burden: The administrative task of constantly monitoring and renewing E-waybills across multiple shipments requires meticulous attention to detail.
- Regulatory Changes: Adapting to frequent regulatory changes regarding E-waybill requirements adds complexity to managing expirations effectively.
- Penalties and Fines: Failure to manage expired E-waybills in accordance with regulations can result in penalties or fines, impacting the bottom line of businesses.
Addressing these challenges demands a proactive approach, including robust systems, diligent monitoring, and a comprehensive understanding of regulatory frameworks to ensure smooth operations within the transportation and logistics sector.
Exemption considerations for specific situations
Exemptions for expired E-waybills might be considered in certain situations, typically contingent upon the specifics outlined in regulations. Some scenarios that could warrant exemption considerations include:
- Force Majeure Events: Instances of unforeseen circumstances, such as natural disasters or political unrest, that impede timely renewal or usage of E-waybills.
- Technical Glitches: System failures or technical issues preventing the timely renewal or generation of E-waybills despite proactive efforts by the transporter.
- Governmental Disruptions: Situations where government-mandated restrictions or disruptions hinder the renewal or usage of E-waybills.
- Specific Industry Exemptions: Some industries might have unique circumstances or operational challenges that could be considered for exemptions under certain conditions.
However, these exemptions typically require substantial documentation and evidence to support the claim for exemption. It’s crucial to adhere to the guidelines and processes stipulated by the regulatory authorities when seeking exemptions for expired E-waybills in specific situations.
E-waybill renewal best practices
Certainly, here are some best practices for E-waybill renewal:
- Proactive Monitoring: Maintain a centralized system or calendar to track E-waybill expiration dates well in advance, ensuring timely renewals.
- Automated Alerts: Set up automated reminders or notifications to prompt renewal procedures ahead of E-waybill expiration dates, reducing the risk of oversights.
- Efficient Communication: Establish clear communication channels among relevant stakeholders, including shippers, transporters, and authorities, to streamline the renewal process.
- Documentation Accuracy: Ensure all necessary details and documentation are accurate and up-to-date when renewing E-waybills to prevent discrepancies or rejections.
- Adherence to Regulations: Stay updated with evolving regulatory requirements and compliance standards to ensure E-waybill renewals align with current guidelines.
- Training and Awareness: Provide training to personnel involved in managing E-waybills, fostering awareness of renewal protocols and the significance of timely actions.
Implementing these best practices can significantly contribute to a smoother and more efficient E-waybill renewal process, minimizing disruptions in transportation operations and ensuring compliance with regulatory frameworks.
Audit and verification of expired E-waybills
Auditing and verifying expired E-waybills is a crucial aspect of regulatory compliance and operational efficiency within the transportation and logistics sector. Here are the steps involved in this process:
- Documentation Review: Conduct a thorough review of expired E-waybills, ensuring all details, including reasons for expiration and any corrective actions taken, are accurately documented.
- Comparison and Analysis: Compare expired E-waybills against the actual transportation events or shipments to verify discrepancies, if any, and understand the impact on operations.
- Compliance Assessment: Verify if the expired E-waybills comply with regulatory requirements and internal policies, ensuring that corrective measures if needed, align with established protocols.
- Rectification Procedures: Identify any issues or deviations found during the audit and initiate corrective actions to rectify discrepancies or non-compliance.
- Continuous Improvement: Use insights gained from the audit to improve internal processes, systems, and training programs to prevent future occurrences of expired E-waybills.
Regular audits and verification of expired E-waybills not only ensure compliance but also contribute to operational efficiency by identifying areas for improvement within the transportation and logistics framework.
Role of technology in E-waybill expiry management
Technology plays a pivotal role in effective E-waybill expiry management within the transportation and logistics domain:
- Automated Tracking: Technology enables automated tracking of E-waybill expiration dates, sending alerts and notifications well in advance to prompt timely renewals.
- Centralized Systems: Utilizing centralized digital platforms or software helps in managing and organizing E-waybill information, making it easier to monitor and renew multiple bills efficiently.
- Real-time Updates: Digital systems provide real-time updates on E-waybill status, ensuring accurate information and facilitating proactive management of expirations.
- Integration with Transport Systems: Integration of E-waybill systems with transportation management systems streamlines processes, reducing manual errors and ensuring compliance.
- Data Analytics: Technology facilitates data analysis of E-waybill usage patterns, allowing for predictive insights and proactive measures to prevent expirations.
- Mobile Applications: Mobile apps offer on-the-go access to E-waybill information, enabling quick updates, renewal submissions, and verification processes from anywhere.
Conclusion
Handling expired E-waybills means following clear steps and having the right paperwork. Renewing these documents on time is super important to keep goods moving smoothly and avoid any problems or fines.
By knowing the rules, sticking to them, and keeping records up to date, businesses can deal with expired E-waybills without any hassle and keep their deliveries on track.
FAQs
Q1: What is an E-waybill, and why does it expire?
An E-waybill is a document required to move goods, detailing the sender, recipient, and goods being transported. It expires after a set period to ensure updated information and compliance with regulations.
Q2: How can I check the expiration status of my E-waybill?
You can verify the expiration status of your E-waybill by logging into the E-waybill portal or through the designated government portal for transportation.
Q3: What happens if my E-waybill expires during transit?
If an E-waybill expires during transit, it can lead to disruptions in the transportation process, potential fines, and complications with regulatory compliance.
Q4: Is it possible to extend the validity of an E-waybill?
In general, E-waybill validity cannot be extended once it has expired. Renewal or generating a new E-waybill is typically required.
Q5: What are the key steps to renew an expired E-waybill?
Renewing an expired E-waybill involves accessing the E-waybill portal, selecting the renewal option, updating necessary information, and generating a new E-waybill with a valid period.
Q6: Are there penalties for using an expired E-waybill?
Yes, using an expired E-waybill can result in penalties, fines, and potential legal consequences, varying based on regional regulations.
Q7: Can I update information on an expired E-waybill?
Generally, an expired E-waybill cannot be updated. Generating a new E-waybill with the correct information is usually required.
Q8: How does managing expired E-waybills impact my business operations?
Mismanagement of expired E-waybills can disrupt logistics, delay shipments, incur fines, and negatively impact the efficiency of your business operations.
Q9: Are there specific documents required to renew an expired E-waybill?
While requirements may vary, commonly needed documents include invoice details, transporter ID, and relevant shipment information for renewal.
Q10: What are the consequences of not addressing expired E-waybills promptly?
Delayed action on expired E-waybills can lead to increased fines, shipment delays, legal complications, and negatively affect business credibility with authorities and clients.
