Legal entities, like individuals running businesses alone or with others, come in different forms—sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations. Registering for Goods and Services Tax (GST) is important for them. It’s like joining a club where businesses contribute a bit of their sales to support public services. Registering is a way of saying, “Hey, I’m part of this, and I’m following the rules.” To join, legal entities need to fill out forms and provide details about what they do. It’s like sharing information about the club you’re in. By registering, businesses can enjoy certain benefits, like claiming back some of the tax they paid on their expenses. It’s a way to be fair and square in the business world.
GST registration for non-resident entities
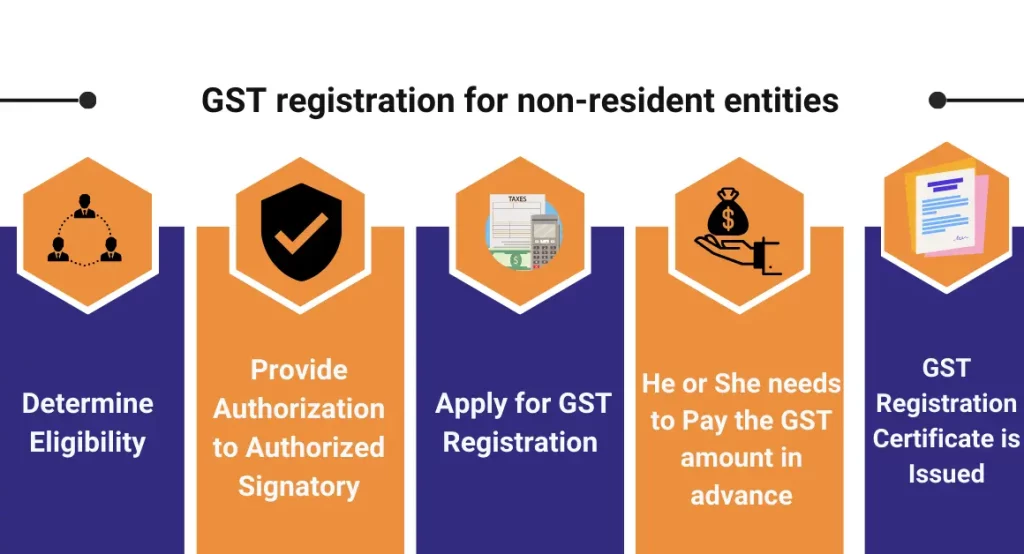
Understanding the Goods and Services Tax (GST) system is key for non-resident businesses in India. GST registration is necessary if you’re a non-resident involved in supplying goods or services in the country. This requirement ensures that non-residents comply with the tax rules related to their transactions within India. Exploring the GST registration requirements for non-residents becomes crucial, as it outlines the specific criteria and steps they need to follow to smoothly integrate into the Indian tax structure. This process not only facilitates legal compliance but also enables non-resident businesses to actively participate in the Indian market.
Here is the simplified process GST registration for Non-resident businesses:
- Step 1- Determine Eligibility
- Step 2- provide Authorization to Authorized Signatory
- Step 3- Apply for GST Registration by accessing official website
- Step 4- He or She needs to Pay the GST amount in advance
- Step 5- GST Registration Certificate is Issued
Types of business entities eligible for NRT GST registration
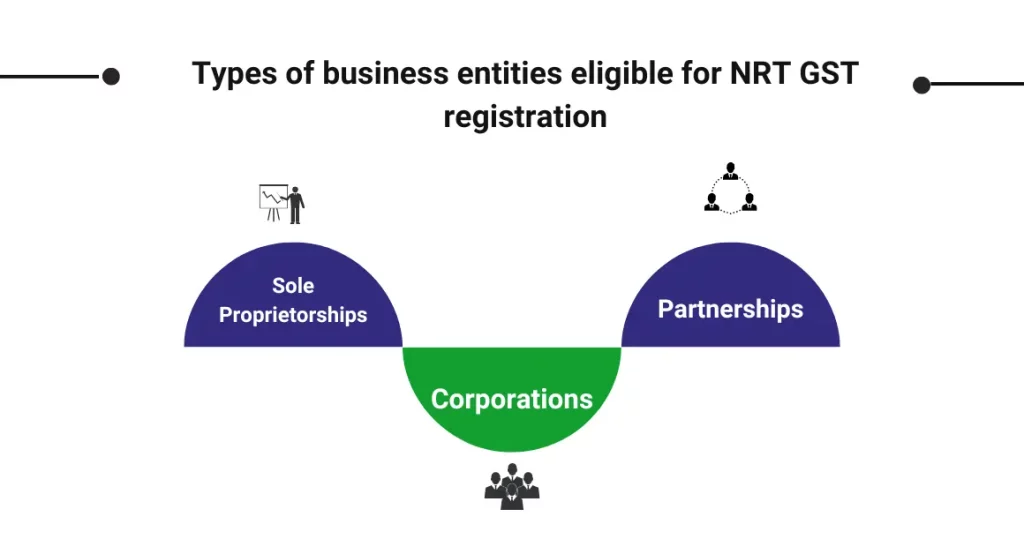
In the context of Goods and Services Tax (GST) registration for non-resident entities (NRT), various types of business entities may be eligible to register based on their structure and activities. The eligibility criteria can differ, and it’s essential to understand how different business structures qualify for NRT GST registration. The primary types of entities that may be eligible include:
-
Sole Proprietorships:
-
-
- Sole proprietorships, often characterized by a single owner managing the business, may be eligible for NRT GST registration if they engage in activities subject to GST in the jurisdiction where registration is sought.
-
-
Partnerships:
-
-
- Partnerships, involving two or more individuals or entities operating a business together, can be eligible for NRT GST registration if their business activities fall under the purview of GST regulations in the relevant jurisdiction.
-
-
Corporations:
-
-
- Corporations, as separate legal entities, may qualify for NRT GST registration if they conduct business activities subject to GST and meet the specified eligibility criteria. This includes considering factors such as turnover, nature of business, and compliance with local regulations.
-
Documents required for NRT GST registration by different entities:
- Permanent Account Number (PAN) or Tax Identification Number of the Applicant
- Proof of Business Incorporation
- The taxpayer needs to provide the following proof of the principal place of business:
- Own Premises- For verification of ownership, documentation like property tax receipts, municipal khata copies, or electricity bills (not older than 3 months) may be necessary for one’s own premises.
- Rented or Leased Premises- A valid Rent/Lease Agreement, along with supporting documents like the lessor’s latest Property Tax Paid Receipt, Municipal Khata copy, or Electricity Bill, is required.
- In cases other than above, 2- A consent letter, accompanied by supporting documents like the consenter’s Municipal Khata copy or Electricity Bill copy, is needed.
- Bank Account Statement
NRT registration process for sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations
| Type of Entity | Steps |
| Sole Proprietorships | 1. Determine Eligibility: Ensure that the sole proprietorship meets the criteria for NRT registration, such as engaging in taxable activities in India or meeting the threshold for GST registration. |
| 2. Gather Required Documents: Collect necessary documents including PAN (Permanent Account Number), proof of address, identity proof of proprietor, and any other documents as required by the tax authorities. | |
| 3. Online Application: Visit the GST portal or relevant tax authority’s website and fill out the online registration form for NRT. Provide accurate information and upload the required documents. | |
| 4. Verification: After submission, the tax authorities will verify the information provided and may request additional documents or clarification if needed. | |
| 5. Issuance of Registration Certificate: Once the verification process is complete, the tax authorities will issue the NRT registration certificate, enabling the sole proprietorship to conduct taxable activities in India. | |
| Partnerships | 1. Determine Eligibility: Ensure that the partnership meets the criteria for NRT registration, such as engaging in taxable activities in India or meeting the threshold for GST registration. |
| 2. Obtain Partner’s PAN: Ensure all partners have a PAN (Permanent Account Number) as it is mandatory for NRT registration. | |
| 3. Collect Required Documents: Gather necessary documents including PAN of partners, partnership deed, proof of address, identity proof of partners, and any other documents as required. | |
| 4. Online Application: Visit the GST portal or relevant tax authority’s website and fill out the online registration form for NRT. Provide accurate information and upload the required documents. | |
| 5. Verification and Certificate Issuance: Similar to the process for sole proprietorships, the tax authorities will verify the information provided and issue the NRT registration certificate upon successful verification. | |
| Corporations | 1. Determine Eligibility: Ensure that the corporation meets the criteria for NRT registration, such as engaging in taxable activities in India or meeting the threshold for GST registration. |
| (LLCs or LLPs) | 2. Gather Required Documents: Collect necessary documents including Certificate of Incorporation, PAN of the corporation, proof of address, identity proof of authorized signatory, and any other documents as required. |
| 3. Online Application: Visit the GST portal or relevant tax authority’s website and fill out the online registration form for NRT. Provide accurate information and upload the required documents. | |
| 4. Verification and Certificate Issuance: The tax authorities will verify the information provided and conduct due diligence on the corporation. Upon successful verification, the NRT registration certificate will be issued, allowing the corporation to operate in India. |
Eligibility criteria for NRT registration based on business structure

When considering Goods and Services Tax (GST) registration for non-resident entities (NRT), the eligibility criteria are crucial and vary based on the specific business structure. Here’s the details:
| Sole Proprietorships | Partnerships | Corporations |
| Legal Requirements and Documentation | Document Required | Documents required |
| – Must be an Indian citizen who pays taxes. | – Proof of Identity (Passport, National Identity Card, etc.) | – Certificate of Incorporation |
| – Register business for GST. | – Proof of Address | – Memorandum and Articles of Association |
| – Open a bank account in the proprietorship’s name. | – Business Registration Documents | – Board Resolution |
| – Tax Identification Number (TIN) | – Proof of Identity of Authorized Representatives | |
| – Bank Account Details | – Proof of Address of Authorized Representatives | |
| – Details of Business Activities | – Tax Identification Number (TIN) | |
| – Financial Statements (Income, Balance Sheets, etc.) | – Business Turnover Details | |
| – Business Turnover Details | – Details of Business Activities | |
| – Authorization Letter | – Financial Statements | |
| – Bank Account Details | ||
| – Authorization Letter | ||
| Overview of eligibility criteria: | ||
| – Age Requirement: At least 18 years old. | ||
| – Citizenship: Must be a citizen or legal resident. | ||
| – Legal Capability: Owner should have legal capacity. | ||
| – Business Purpose: Must have a clear purpose. | ||
| – Business Name: Choose a unique name. |
Impact of NRT GST registration on taxation and compliance
The impact of non-resident entity (NRT) GST registration on taxation and compliance can vary based on the jurisdiction and the specific regulations in place. However, here are some general impacts to consider:
- Tax Liability:
-
-
- NRT GST registration typically implies that the non-resident entity is now subject to the local Goods and Services Tax regulations. This means they are required to collect GST on taxable supplies and remit it to the tax authorities.
-
- Input Tax Credits:
-
-
- Registered NRTs may be eligible to claim input tax credits for the GST paid on their business expenses. This can help offset the GST liability on their sales.
-
- Compliance Obligations:
-
-
- NRTs must comply with the local tax laws and regulations, including filing regular GST returns and maintaining proper accounting records. This can involve additional administrative tasks and responsibilities.
-
- Record-Keeping Requirements:
-
-
- There may be specific record-keeping requirements imposed on NRTs, including the retention of invoices, receipts, and other relevant documents for a specified period. This is crucial for audits and compliance verification.
-
- Audit and Verification:
-
-
- NRTs may be subject to audits or verification processes by tax authorities to ensure compliance with GST regulations. This can involve providing documentation and evidence to support GST filings.
-
- Changes in Pricing and Contracts:
-
-
- The inclusion of GST in the pricing structure may necessitate adjustments in pricing strategies. Contracts and agreements may need to be reviewed and updated to account for GST implications.
-
- Impact on Profitability
-
- NRT GST registration can have financial implications for the business. The costs associated with compliance and the potential impact on pricing and competitiveness need to be considered in terms of overall profitability.
- Cross-Border Transactions:
- NRT GST registration may affect how cross-border transactions are treated for tax purposes. Understanding the implications of GST on international business activities is essential.
- Customs and Import/Export Considerations:
- NRTs involved in the import or export of goods may need to navigate customs regulations and ensure compliance with GST requirements related to international trade.
Conclusion:
In summary, whether you’re a person running a business alone, with others, or in a big company, it’s crucial to follow the rules for non-resident entity GST registration. Know the specific criteria for your business type, like doing taxable activities. Collect the needed documents, like IDs and financial papers, and go through the registration process. Once registered, you’ll be part of the local tax system, responsible for things like GST. Keep good records, as audits might happen. It could affect how you set prices and manage contracts. Remember, following the rules is a must to avoid legal problems and keep your business running smoothly.
Also Read: How to Calculate GST in an Excel Sheet: Step-by-Step Guide
FAQ’s:
-
Who is required to undergo GST registration for non-resident entities (NRT)?
- Non-resident entities engaging in taxable activities within a jurisdiction are generally required to undergo GST registration to comply with local tax regulations.
-
What types of business entities are eligible for NRT GST registration?
- Sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations are among the common business entities eligible for NRT GST registration based on their structure and business activities.
-
Can you provide an overview of the NRT registration process for sole proprietorships?
- The NRT registration process for sole proprietorships involves submitting relevant documents, such as proof of identity, business registration, and financial statements, to the local tax authorities. The process may vary by jurisdiction.
-
What are the eligibility criteria for NRT registration based on the business structure?
- Eligibility criteria include engaging in taxable activities, meeting turnover thresholds, and complying with local regulations. Criteria may differ for sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations.
-
What documents are required for NRT GST registration by corporations?
- Documents typically include the certificate of incorporation, memorandum and articles of association, proof of identity for authorized representatives, financial statements, and other relevant documents as specified by local tax authorities.
-
How does NRT GST registration impact taxation for non-resident entities?
- NRT GST registration subjects entities to local tax laws, making them liable to collect and remit GST on taxable supplies. It may also allow for claiming input tax credits on eligible expenses.
-
What is the impact of NRT GST registration on compliance obligations?
- NRTs must comply with local tax regulations, including filing regular GST returns, maintaining proper records, and undergoing potential audits or verification processes.
-
Are there specific record-keeping requirements for entities with NRT GST registration?
- Yes, entities are typically required to maintain records such as invoices, receipts, and other relevant documents for a specified period to ensure compliance with GST regulations.
-
How does NRT GST registration affect pricing and contracts for businesses?
- NRT GST registration may necessitate adjustments in pricing strategies to account for GST. Contracts and agreements may need to be reviewed and updated to reflect these changes.
-
Can non-compliance with NRT GST registration lead to legal consequences?
- Yes, non-compliance with GST regulations can result in penalties and legal consequences. It is crucial for entities to stay informed about tax laws and fulfill their obligations to avoid legal issues.

