Introduction to GST in Sales Invoicing
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) has replaced several indirect levies. It significantly impacts the procedures used for sales transaction invoicing. Since GST may harmonize taxes on products and services, promote transparency, and make compliance easier, it is essential to sales invoicing.
Businesses must understand GST on sales invoices to properly manage the tax environment and uphold compliance with existing legislation.
This article explores the GST Impact on Invoices. Also, we will examine the main benefits and advantages it brings to businesses, making taxes simpler and more consistent.
Understanding GST and its Impact on Invoicing
Goods and Services Tax is a value-added tax charged at all stages in the supply chain. The efforts of the GST to establish a unified tax system that is easier for businesses to use and for tax authorities to oversee are clear indications of the GST Impact on Invoices. The key aspects include:
- Unified Tax Structure: The GST replaces several other indirect taxes, unifying the tax structure. The application of a single tax on invoices that cover both goods and services simplifies the taxation process.
- GST Identification Numbers (GSTIN): Companies must provide their individual GSTIN on all Sales invoices. It helps tax authorities swiftly check information and to identify the taxpayers.
- Inter-State and Intra-State Transactions: The applicable GST rates for a transaction will vary depending on whether it is intrastate or interstate. The invoice has to include this information. This difference is necessary to determine tax liabilities and jurisdiction.
- Clear Taxable Value and GST Rates: Invoices must include the taxable amount of goods or services and relevant GST rates. This transparency helps customers and businesses to understand the impact of taxes on each transaction.
- Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM): The reverse charge method (RCM) requires the invoice to specify if the recipient has the financial responsibility for the taxes owed. It shifts the beneficiary’s tax payment responsibility.
- Electronic Invoicing (e-invoicing): Several nations implement E-invoicing under the Goods and Services Tax. Companies create bills digitally, which increases productivity, lowers mistakes, and allows tax authorities to monitor in real time.
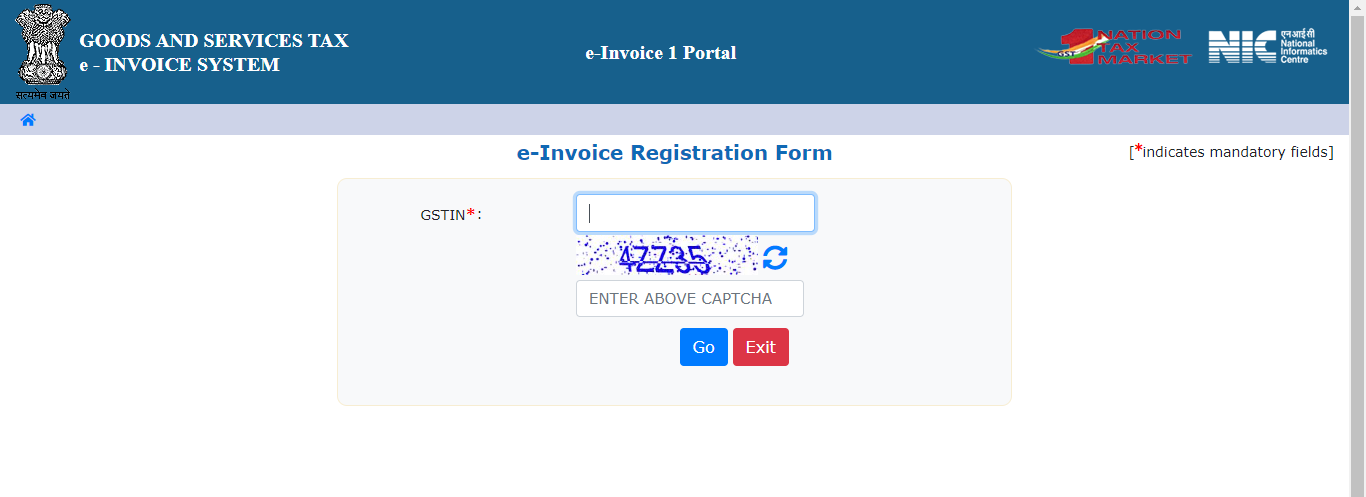 E-invoice Registration Form 1
E-invoice Registration Form 1
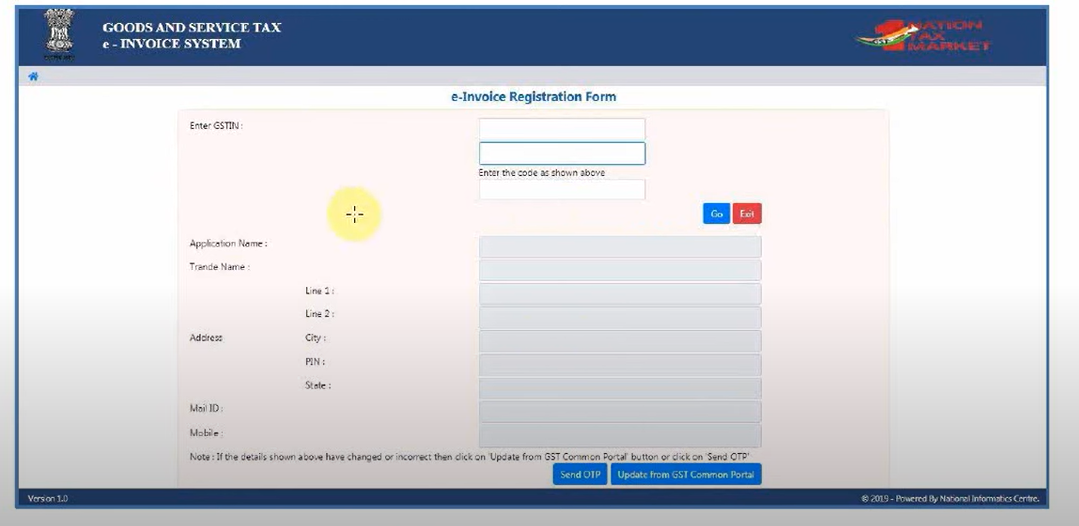
E-invoice Registration Form 2
- Place of Supply: The invoice must mention the place of supply while dealing with interstate transactions. This data is essential to determine the accurate GST rate and ensure local tax laws comply with them.
- Input Tax Credit (ITC): Businesses can apply for Input Tax Credit using the information on the invoice. Utilizing ITC and minimizing the resulting accumulation of taxes requires accurate and GST-compliant invoicing.
- Compliance and Record-Keeping: GST imposes strict invoice conformity standards. Businesses must follow guidelines, keep records for a given amount of time, and file returns on time. Penalties may result from noncompliance.
Also Read: Impact of GST: Invoice, Simplified Tax System and Reduce Compliance Burden
Benefits of GST in Sales Invoices
There are several significant advantages for companies from the Goods and Services Tax (GST) introduction in sales invoicing. The following are the main benefits of GST invoicing:
| Uniformity in Tax Rates |
|
| Elimination of Cascading Effect |
|
| Transparency |
|
| Easier Interstate Transactions |
|
| Reduction in Tax Evasion |
|
| Compliance and Legal Certainty |
|
Also Read: Benefits of GST for Small Business
Simplification of Invoicing Processes under Goods and Services Tax
A more simple and uniform invoicing system is the outcome of simplifying the intricacies brought forth by several indirect taxes under one single tax structure. Under GST, businesses now produce invoices that explicitly state the appropriate GST rates as well as the taxable amount of the products or services.
To ensure that taxes are applied exclusively to the net value, the removal of cascading taxes has further simplified computations. Companies may deduct the taxes they pay on inputs from the output taxes they owe with Input Tax Credit (ITC), which encourages thorough recordkeeping.
In addition, the mandate for companies to provide their own GST Identification Number (GSTIN) on invoices ensures precise taxpayer monitoring and identification. The uniform use of SAC codes for services and HSN codes for goods enables standardized classification. This helps with accurate tax computations.
In general, the transition to electronic invoicing and the removal of regional tax rate disparities have been crucial in streamlining the invoicing procedures, promoting transparency, and promoting an efficient and compliant business climate under the GST system.
Role of GSTN (Goods and Services Tax Network)
The GSTN is an electronic online infrastructure to make the GST easier to apply. It provides a channel via which taxpayers and the GST authorities may communicate electronically and file taxes. A GSTN has several roles, including:
-
One Window for Paying Taxes:
- The unified platform that GSTN offers allows all taxpayers to file their taxes online, which is one of its main responsibilities.
- Streamlining the process of providing individuals with the information and documents required to file their taxes helps to expedite the process.
-
Management of GST:
- Apart from offering a unified tax reporting platform, GSTN has significant importance in the administration of GST legislation. It facilitates the government’s ability to monitor the GST revenues obtained from taxpayers and guarantee that the right amount of taxes is collected.
- The GSTN assists the government in keeping updated on taxpayer adherence to the GST legislation.
-
Safe Online Payment Gateway:
- Additionally, GSTN offers companies a safe platform for handling their GST accounts. This enables them to monitor the amounts and collections of their GST.
- Businesses can also get the information they require from GSTN to file their GST returns. Additionally, it facilitates their ability to pay and collect under the GST system.
Compliance and Legal Aspects of GST Invoicing
Businesses must produce GST-compliant invoices for their transactions in many countries to file GST returns, obtain input tax credits, and adhere to other regulatory obligations. While invoicing auditing, Tax authorities utilize the data on the GST invoice to confirm that the right amount of GST has been collected and paid. The following are some essential components of a GST invoice:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Adherence to current rules is crucial for businesses to prevent penalties and ensure optimal functioning. The following are important legal and regulatory factors related to GST invoicing:
- Invoices must include the recipient’s and supplier’s Goods and Services Tax Identification Numbers (GSTINs). This ensures the correct identification of the transaction’s parties.
- Businesses are unable to claim the Input Tax Credit if their invoices do not have the correct documentation. Incomplete or incorrect invoices may make it more difficult to get input tax credits, increasing the overall amount owed.
- Invoices, supporting documentation, and other relevant records must be kept up to date by businesses for a certain time. Tax authorities may audit these data, and fines may result from noncompliance.
- An essential part of completing GST returns is submitting invoices. Complying with regulations requires timely and accurate return filing, including GSTR-1 for outbound supplies and GSTR-3B for summary returns.
Impact on Business and Economy
With the introduction of GST, many indirect taxes were replaced, simplifying the taxation process from producers to end users. India’s economy grew at one of the quickest rates in the world because of this historic decision.
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) led to a notable rise in government revenue, enhanced tax compliance, decreased tax evasion, and facilitated effective monitoring. Also, it impacts several business sectors, including:
- Manufacturing Sector: Simplified GST sales invoicing guarantees smooth credit flow, lessens complexity, and increases transparency. Manufacturers gain from higher competitiveness and simpler regulatory burdens.
- Retail Industry: Retailers can minimize paperwork and avoid tax cascade effects by using GST Invoicing, which streamlines taxation. This results in lower costs and improves supply chain efficiency.
- IT Sector: GST invoicing makes compliance easier by promoting a consistent tax structure. It develops and innovates by making the financial ecosystem more transparent for IT companies.
- Real Estate: GST invoicing brings clarity to tax structures in real estate transactions, reducing tax evasion. This fosters trust among and promotes a more organized and accountable sector.
- Automobile Industry: Under the GST, automobiles gain from streamlined invoicing since it eliminates cascading taxes, lowers logistical costs, and promotes pricing homogeneity, all of which increase market competitiveness.
- Textile and Apparel Sector: For textile enterprises, GST invoicing streamlines tax computations and eases compliance. This increases the sector’s cost-effectiveness and availability of loans.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: GST invoicing ensures transparency and accountability in pharmaceutical transactions. The seamless credit flow helps in cost management and encourages research and development activities.
- Hospitality and Tourism: The hospitality industry benefits from simplified GST invoicing since it lowers tax complexity. This improves consumer satisfaction, boosts tourism, and fosters industry expansion.
- Agricultural Sector: Agricultural transactions become more transparent due to GST invoicing, which also lowers tax leaks. It guarantees a fair pricing system and facilitates farmers’ access to a huge market.
- E-commerce: For e-commerce companies, GST invoicing makes tax compliance easier. It guarantees the effectiveness of tax collection, fosters growth in online trade, and creates an equal chance for vendors.
Adoption Challenges and Solutions
Several challenges arise in the implementation of GST invoicing, such as the need for enterprises to adjust to a single system, technological readiness concerns, and initial confusion resulting from a complicated tax structure.
Various factors impact the smooth transition to GST invoicing, including obstacles to compliance and resistance to change. Strong awareness programs and training initiatives were essential to educating businesses about GST obligations to address GST Invoicing Challenges.
It is necessary to implement technological support and user-friendly GST invoicing software to improve compliance and expedite procedures.
Future of GST and Invoicing
Technological developments and a persistent emphasis on simplification will significantly influence the future of GST and invoicing. Digital tools and automation are essential for increasing overall transparency, decreasing errors, and streamlining compliance procedures.
It may be possible to improve the system to make it more user-friendly for taxpayers as companies and tax authorities adapt to shifting demands.
Furthermore, there is a chance that initiatives to standardize invoices internationally will pick up speed and make cross-border transactions easier. In general, the future seems promising for a more streamlined, technologically advanced, and internationally integrated GST and invoicing environment.
Also Read: The Future of GST in the Era of Web3
Conclusion
In summary, GST is essential in encouraging sales invoicing since it offers a uniform framework that streamlines transaction documentation. The incorporation of GST into Invoicing mitigates the problems associated with GST invoicing Auditing and streamlines the overall sales process.
It is necessary to recognize and resolve the GST invoicing challenges to obtain overall benefits. In the context of sales transactions, the relationship between GST and invoicing has the potential to promote increased efficiency, transparency, and compliance as businesses adjust and technology develops.
FAQs
Q1. What is GST, and how does it affect invoices for sales?
The Goods and Services Tax, or GST, is a single tax system that takes the role of several other indirect taxes. It streamlines sales invoicing by offering a uniform structure for taxes.
Q2. Do GST-compliant invoices have to meet any particular requirements?
Yes, A GST-compliant invoice needs to have information such as the GSTIN, the description of the products or services, the HSN code, and the relevant tax rates.
Q3. In what way does GST help firms with sales invoicing?
GST simplifies the sales process by lowering tax requirements, enhancing transparency, and offering smooth input tax credits.
Q4. What difficulties can companies have when including GST in their invoices?
Difficulties might include the need to overcome early adaption barriers, make technology improvements, and guarantee appropriate classification of commodities or services.
Q5. Can I get a credit for input taxes on goods that are shown on my sales invoice?
Yes, as long as companies follow the guidelines and laws of GST, they are eligible to claim input tax credits on purchases.
Q6. Are some sales transactions exempt from the Goods and Services Tax?
Yes, There are certain commodities and services exempt from the Goods and Services Tax. Companies must be aware of these to guarantee proper billing.
Q7. What is the effect of GST on international sales and billing?
The GST ensures a unified tax structure and makes cross-border sales easier by including provisions for both intrastate and interstate transactions.
Q8. What is the function of technology in sales invoicing that complies with GST?
Technology is essential for maintaining accuracy, automating billing procedures, and enabling easy GST compliance.
Q9. Can I fix mistakes on my sales invoice after it’s been sent out?
Under certain restrictions, businesses can use credit or debit notes under GST to correct mistakes on their invoices.
Q10. What role does GST play in lessening the amount of tax avoidance in sales transactions?
The traceability and transparency of GST, together with its strict compliance requirements, help to reduce tax avoidance in sales transactions.
