Introduction
GST is a comprehensive indirect tax introduced to replace multiple taxes from both central and state governments, aiming for a unified tax structure. It covers various goods and services with rates like 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%. The three main types are Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST) for intra-state transactions, State Goods and Services Tax (SGST) for intra-state transactions, and Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST) for inter-state transactions and imports.
We will deep dive into the details of GST calculations for interstate and intrastate transactions.
Understanding Interstate Transactions
Interstate transactions involve buying or selling goods or services between two different states within a country. In simple terms, when a business in one state sells products to a buyer in another state, it’s considered an interstate transaction.
Example: Imagine a bakery in Karnataka sells cakes to a customer in Maharashtra. Since Karnataka and Maharashtra are different states, this is an interstate transaction. In such cases, Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST) is applied to the transaction, and the revenue goes to the Central Government. The IGST aims to simplify taxation for businesses involved in transactions across state borders.
GST for interstate transactions involves Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST). IGST is a component of GST that ensures seamless taxation on transactions occurring between states. It is collected by the central government and later distributed to the destination state.
Businesses engaging in interstate transactions need to consider the implications on pricing, logistics, and compliance and must be aware of the legal and regulatory framework governing such transactions. Compliance with both central and state regulations is essential to avoid legal issues.
Also Read: Understanding Inter-State Transactions: Definition And Scope
Key Aspects of Intrastate Transactions
It refer to the essential elements that characterize transactions involving the movement of goods or services within the boundaries of a single state. Here’s a breakdown of the key aspects:
- State-Specific Regulations:
- Each state has its own rules for transactions happening within the state, covering taxes, documentation, and compliance.
- GST Implications:
- The application of GST in transactions within a state is influenced by the state’s tax rates, involving Central GST (CGST) and State GST (SGST) or Union Territory GST (UTGST).
- Place of Supply Determination:
- Figuring out where the transaction happens within a state is crucial for calculating GST, as it determines the state taxes applied.
- Compliance Requirements:
- Businesses in intrastate trade must follow GST rules and state-specific regulations, ensuring proper documentation, invoicing, and compliance with additional state requirements.
- Taxation Framework:
- The taxation framework for intrastate transactions deals with the movement and use of goods or services within state borders, requiring an understanding of the state’s specific tax rules.
- GST Components:
- Unlike interstate transactions with IGST, intrastate transactions involve separate GST components—CGST and SGST or UTGST—which businesses must be aware of for accurate tax calculations.
- Logistical Considerations:
- Efficient transportation and supply chain strategies tailored for movement within a state are crucial for businesses engaged in intrastate trade.
- Impact on Pricing Strategies:
- State-specific tax rates and regulations can impact how businesses price their products or services in intrastate transactions, requiring careful consideration for competitiveness.
Factors Influencing GST Calculation

The amount of tax you pay on things you buy or services you use can depend on different factors. It could be the type of thing you’re buying, where you’re buying it, how much it costs, and what the government decides is the right tax for it. If you’re a business, you can sometimes get back the tax you paid on things you used to make or sell your products. It’s important to know the rules and any changes the government makes in how taxes work. Here’s the details:
- Type of Goods or Services:
- Different goods and services attract varying GST rates, determined by the nature of the product or service.
- Location of Transaction:
- The transaction’s location is crucial; GST rules differ between states or regions, classifying transactions as interstate or intrastate.
- Transaction Value:
- The total transaction value is significant; GST is a percentage of this value, so higher transactions result in higher GST amounts.
- Government-Set Tax Rates:
- Governments set specific tax rates for various goods and services, and understanding these prescribed rates is essential for accurate GST calculation.
- Place of Supply Rules:
- The deemed location of supply—whether it’s the supplier’s, recipient’s, or a third party’s location—affects applicable tax rates.
- Also read: What Are The Different Rules That Apply To The Place Of Supply Of Goods?
- Input Tax Credit (ITC):
- Businesses claiming Input Tax Credit for GST paid on inputs, like raw materials, influences the effective GST liability.
- Exemptions and Special Provisions:
- Certain goods or services may be exempt from GST, and understanding special provisions for specific transactions is critical for accurate calculation.
Also Read: Demystifying GST Calculations: A Comprehensive Guide For Sales And Purchases
Methods of GST Calculation for Interstate Transactions
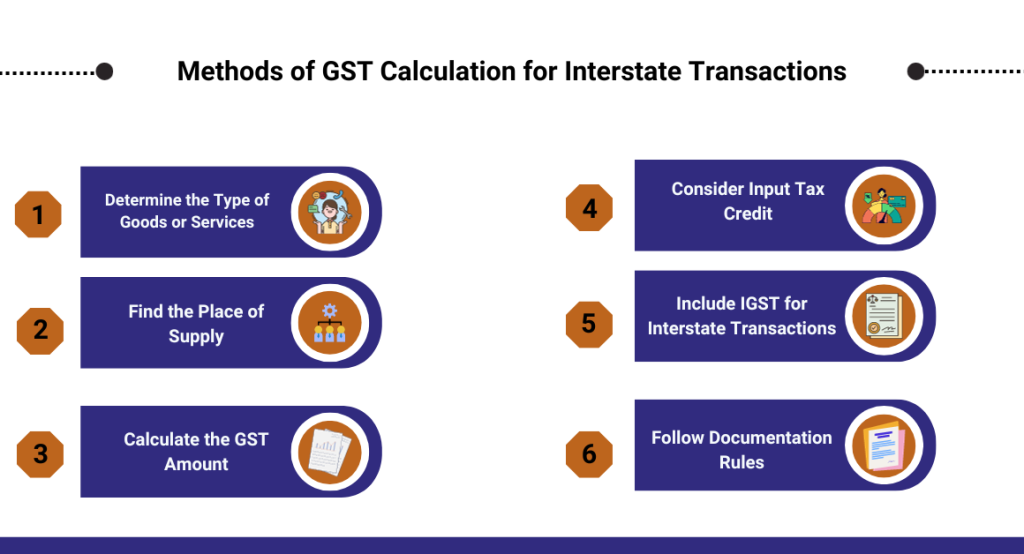
Calculating GST for transactions between different states involves a few steps:
-
Determine the Type of Goods or Services:
- Different things have different tax rates. First, figure out what you’re dealing with.
-
Find the Place of Supply:
- Decide where the goods or services are being used. This helps know which state’s GST rules apply.
-
Calculate the GST Amount:
- Once you know the type and place, use the GST rate for that thing to find out how much GST needs to be paid.
-
Consider Input Tax Credit:
- If you paid GST on things you bought for your business, you might get some money back. This is called Input Tax Credit.
-
Include IGST for Interstate Transactions:
- In interstate deals, there’s something called Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST). This is the total GST, combining both the central and state portions.
-
Follow Documentation Rules:
- Keep proper records and documents related to the transaction. This is important for compliance and claiming benefits like Input Tax Credit.
Methods of GST Calculation for Intrastate Transactions
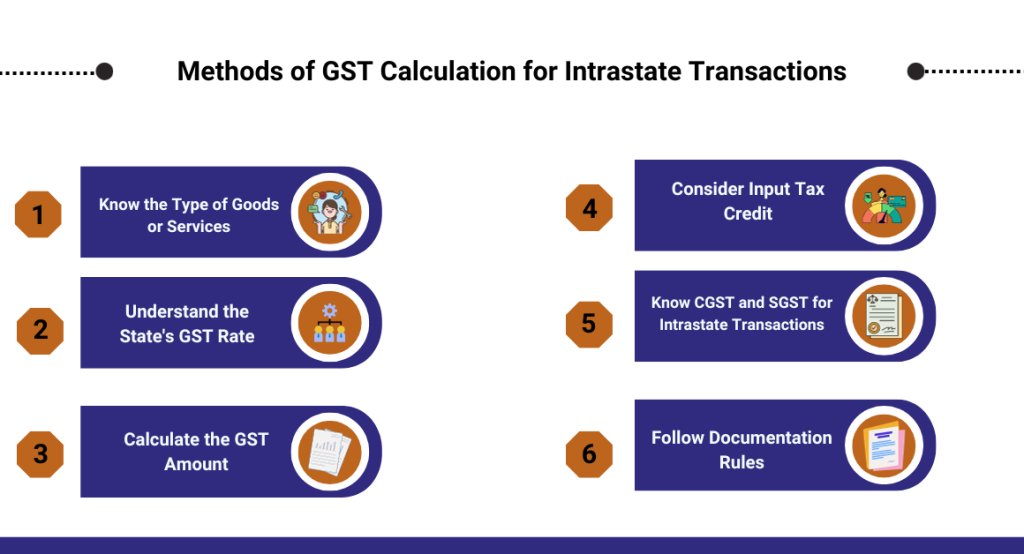
Calculating GST for transactions within the same state involves a few simple steps:
-
Know the Type of Goods or Services:
- Different things have different tax rates. First, figure out what you’re dealing with.
-
Understand the State’s GST Rate:
- Every state can set its own GST rate. Check the rate for your state; that’s the percentage you’ll use.
-
Calculate the GST Amount:
- Once you know the type and the state rate, calculate the GST by applying that percentage to the transaction value.
-
Consider Input Tax Credit:
- If you paid GST on things you bought for your business, you might get some money back. This is called Input Tax Credit.
-
Know CGST and SGST for Intrastate Transactions:
- Unlike interstate deals, intrastate transactions involve Central GST (CGST) and State GST (SGST). Add both to get the total GST.
-
Follow Documentation Rules:
- Keep proper records and documents related to the transaction. This is important for compliance and claiming benefits like Input Tax Credit.
These steps help in figuring out the right amount of GST to pay or charge for transactions happening within the same state.
Also Read: Place Of Supply And Documentation In Intra-State Transactions: Invoices And Supporting Documents
Challenges in GST Calculation for Interstate and Intrastate Transactions
Calculating GST for transactions, whether they are between different states (interstate) or within the same state (intrastate), comes with a few challenges:
-
Varying Tax Rates:
- Different states may have different GST rates. Figuring out the right rate for the type of goods or services can be challenging.
-
Complex Place of Supply Rules:
- Determining the place where the goods or services are being used (place of supply) is crucial. Complex rules can make this a challenging aspect of GST calculation.
-
Navigating Interstate and Intrastate Distinctions:
- Understanding whether the transaction is interstate or intrastate is important. The rules and calculations can vary, and misclassification can lead to errors.
-
Input Tax Credit Management:
- Managing Input Tax Credit, where you get money back for GST paid on business purchases, can be challenging. Keeping accurate records is crucial.
-
Documentation Compliance:
- Both interstate and intrastate transactions require proper documentation. Meeting compliance standards and keeping thorough records can be demanding.
-
Changes in GST Laws:
- GST laws and regulations may change. Staying updated with these changes and ensuring compliance with the latest rules is a persistent challenge.
-
Technology and Software Adaptation:
- Using the right technology and software for GST calculations can be challenging, especially for small businesses. Implementing and adapting to new systems may pose difficulties.
-
Impact on Pricing Strategies:
- The varying tax rates and complex calculations can affect how businesses price their goods or services. Striking a balance between competitiveness and profitability can be a challenge.
-
Educating Staff and Businesses:
- Ensuring that staff and businesses understand the intricacies of GST calculations is a challenge. Education and training are essential to avoid mistakes.
-
Handling Exemptions and Special Cases:
- Some goods or services may be exempt from GST, and there can be special cases. Knowing and appropriately handling these exemptions and special scenarios is challenging.
Conclusion
In conclusion, getting the GST (Goods and Services Tax) calculations right is super important, whether you’re dealing with other states or staying within your own state. It’s like making sure all the pieces of a puzzle fit together. The rates can be different, the rules can be tricky, and the whole process can be a bit of a puzzle. But when you figure it out accurately, it helps businesses stay fair and square with taxes, making sure they pay or charge the right amount. This isn’t just about numbers; it’s about playing by the rules and making sure everyone gets a fair deal. So, whether you’re selling things within your state or sending them across borders, accurate GST calculations are the key to a smooth and fair business journey.
Also Listen: Undеrstanding how is GST calculatеd in MRP
FAQ’s
-
What is GST, and why is it important for transactions?
GST stands for Goods and Services Tax. It’s a crucial tax for transactions because it simplifies the tax system and makes sure everyone pays a fair share.
-
How are interstate transactions different from intrastate transactions?
Interstate transactions happen between different states, while intrastate transactions occur within the same state.
-
Can you explain why knowing the place of supply is important for GST calculation?
Sure! The place of supply helps decide which state’s GST rules apply, and that’s crucial for calculating the right amount of tax.
-
What are the key things affecting GST calculation?
The type of goods or services, the state’s GST rate, and the total transaction value are the main things influencing GST calculation.
-
How do you calculate GST for transactions between different states?
For interstate transactions, you use something called Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST). It’s like combining both central and state GST.
-
And what about transactions within the same state? How do you calculate GST for those?
In intrastate transactions, you use Central GST (CGST) and State GST (SGST) or Union Territory GST (UTGST). You add both to get the total GST.
-
Why is keeping proper documentation important for GST calculations?
Good records and documents help businesses stay on the right side of the law, claim benefits like Input Tax Credit, and show they’re following the rules.
-
What challenges can businesses face when calculating GST for different states?
Varying tax rates, confusing place of supply rules, and managing Input Tax Credit can be tricky for businesses dealing with interstate transactions.
-
How do changes in GST laws affect businesses?
Changes in GST laws mean businesses need to stay updated and make sure they’re following the latest rules to avoid mistakes and stay compliant.
-
Why does accurate GST calculation matter so much for businesses?
Accurate GST calculations mean businesses pay or charge the right amount of tax. It’s not just about numbers; it’s about playing fair, following the rules, and making sure everyone gets a fair deal.

