The goods and services tax (GST) has transformed the indirect tax system in India by replacing multiple taxes with a single, unified tax. It brought transparency and efficiency to the tax regime with its own set of rules and regulations. Filing returns as specified is an important component of compliance under GST. GSTR-9 is one such return. It is an important return as it helps the government monitor the compliance of taxpayers. For taxpayers, it helps in maintaining accurate records of their GST transactions and also ensures compliance. Here we discuss the filing frequency and due dates for GSTR-9.
What is GSTR-9 annual return?
GSTR-9 is an annual return that has to be filed by all taxpayers registered under the goods and services tax regime in India. It is a summarized return that contains consolidated details of all the returns filed under GST by a tax payer during a financial year.
Who should file the GSTR-9 return?
All taxpayers registered under GST are required to file GSTR-9. But the following persons are exempt from filing this return:
- Taxpayers who have opted for the composition scheme
- Casual taxable persons
- Input service distributors
- Non-resident taxable persons
- Persons paying TDS or TCS under Section 51 of the CGST Act
Due Date for filing GSTR-9
Rule 80 of the CGST Rules specifies that every registered taxpayer is liable to file the GSTR-9 annual return on or before the 31st of December of the next financial year. Non-filing and late filing of the return can result in late fees, interest, and other penalties.
Penalties for late filing of GSTR-9
As per Section 47(2) of the CGST Act, 2017, any registered person who fails to furnish the annual returns within the due date is liable to pay a late fee of Rs. 200/- (CGST-Rs. 100/- and SGST-Rs. 100/-) per day. There is no late fee for IGST. Therefore, it is crucial for taxpayers to file their returns by the due date to avoid penalties and ensure compliance.
Pre-requisites for filing GSTR-9
Taxpayers must ensure timely submission of GSTR-1, GSTR-3B, or GSTR-4 returns as per the classification of the taxpayer. It is also important for the taxpayer to clear any outstanding dues; otherwise, the taxpayer will not be able to file the GSTR-9.
Structure of GSTR-9
The return is divided into six parts, containing altogether 19 tables with consolidated information about the inward and outward supplies, the applicable GST rate, the tax applicable, and the amount paid on the supplies.
| Part I |
Basic details: This part comprises the basic details of the taxpayer, like the financial year, GSTIN, legal name, and trade name. |
| Part II |
Details of outward and inward supplies: This part consists of details of advances and inward and outward supplies made during the financial year on which tax is payable in Table 4.
Table 5 consists of details of advances and inward and outward supplies made during the financial year on which tax is not payable.
|
| Part III |
Details of ITC for the financial year |
|
Table 6 consists of details of ITC availed during the financial year. |
|
Table 7 consists of details of ITC reversed and ineligible ITC for the financial year. |
|
Table 8: Other ITC-related information |
| Part IV |
Details of tax paid as declared in returns filed during the financial year: Table 9 consists of details of tax paid as declared in the returns filed during the financial year. |
|
Part V
|
Particulars of the transactions related to the previous financial year that have been amended during April to September of the next financial year or up to the date of filing the annual return, that is, December 31st, whichever is earlier
Table 10 consists of supplies, tax declared through amendments, plus the net of debit notes.
Table 11 consists of supplies, tax reduced through amendments, less the net of credit notes.
Table 12 consists of the reversal of ITC availed during the previous financial year.
Table 13 consists of ITC availed for the previous financial year. Table 14: Differential tax paid on account of the declaration in table 10 and
Table 14 consists of differential tax paid on account of the declarations in tables 10 and 11 above.
|
| Part VI |
Other Information: This part consists of the following tables:
Table 15 consists of particulars of demands and refunds.
Table 16 consists of information on supplies received from composition taxpayers, deemed supplies under Section 143, and goods sent on an approval basis.
Table 17 consists of an HSN-wise summary of outward supplies.
Table 18 consists of a HSN-wise summary of inward supplies.
|
At the end of the return, the taxpayer has the option to pay any additional liability declared in this form. This can be done through Form DRC-03. The taxpayer has to select the annual return in the drop-down provided in Form DRC-03.
Steps to file GSTR-9
The taxpayer has to follow these steps to file GSTRS-9 online in the GST portal:
Step 1:Navigate to the GST portal at https://www.gst.gov.in/ and login with valid credentials.
Step 2: Go to Service>Returns>Annual Returns
Step 3: Select the relevant financial year and click on prepare online
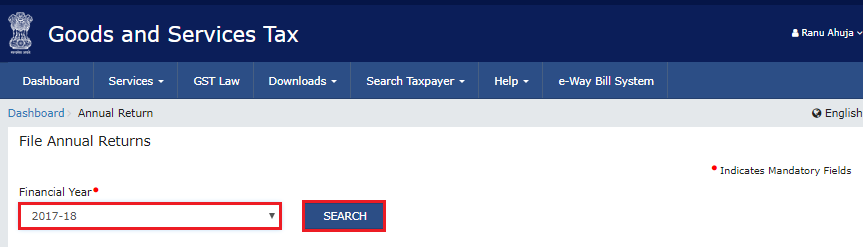
Step 4: Answer the question of whether to file a NIL return. For a regular return, data from GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B is auto-populated in the GSTR-9 form. Click ‘Next’
Step 5: Then the ‘Annual returns for normal taxpayers’ page is displayed.
Step 6: Fill in the required details in each section. The summary of the details in excel or pdf format can be viewed by clicking the ‘Preview’ option.

Step 7: Proceed to ‘Compute liabilities’ and the ‘late fee payable and paid’ will appear. Along with it, the available cash balance will be shown in the ‘Electronic Cash Ledger’.
If the cash balance is less than the tax liability, the details will be shown in the ‘cash required’ section.
Step 8: Click on the ‘create challan’ button. The challan will be auto-populated.
Step 9: After selecting the payment method, click on ‘generate challan’.
Step 10: Click on ‘preview draft GSTR-9 (pdf)’ and download the form.

Step 11: After checking the declaration box and authorized signatory, click on the ‘File GSTR-9’ button.
How to check the status of GSTR-9
To check the status of GSTR-9, the taxpayer has to go through the following steps:
1. Login to the GST portal
- Go to ‘services>returns>track return status
- Enter the return filing period and the ARN, and the status of the GSTR-9 is shown.
(more…)