The Goods and Services Tax, popularly known as the GST, is an indirect tax that replaced many indirect tax systems in India, including the excise duty, VAT, and services tax, among others. It is an indirect form of tax or consumption-based tax levied by the Government of India on all the goods and services parties of a supply chain.
Historically, the Goods and Services Tax was introduced in the year 1999 by the government of India under the Prime Ministership of Atal Bihar Vajpayee. He set up a board under the Finance Minister of West Bengal, Asim Dasgupta, to comprehensively establish a GST model. However, it failed to come to fruition.
However, in 2017, the National Democratic Alliance (NDA) government, led by the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), introduced the GST Bill. The Act came into effect on 1st July 2017 and is now a multi-stage, complete, destination-based tax that is levied on every value addition.
From a legal perspective, the GST provisions are inserted in the Constitution of India by the Hundred and One Constitutional Amendment Act. Article 269A of the Constitution mentions that the GST on supplies in the course of interstate trade or commerce shall be levied and collected by the Government of India.
Moreover, the GST shall be between the Union and the States as directed by relevant laws based on the recommendations of the Goods and Services Tax Council.
 The information provided is used by the property registrar to gather information about the parties to real estate transactions over a certain threshold. Advanced data analysis is made possible by every financial transaction connected to the PAN established with the tax department. Furthermore, information is obtained from a number of government agencies, such as the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, the Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN), and SEBI.
The roaring success of GST and the invaluable data provided by the system knows no bounds. It has helped tax administration in ways that vouch for a more united India with an improved taxing landscape.
But before we get into the lens of administration, let’s take a closer look at the reasons behind the wide acceptance of GST!
The information provided is used by the property registrar to gather information about the parties to real estate transactions over a certain threshold. Advanced data analysis is made possible by every financial transaction connected to the PAN established with the tax department. Furthermore, information is obtained from a number of government agencies, such as the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, the Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN), and SEBI.
The roaring success of GST and the invaluable data provided by the system knows no bounds. It has helped tax administration in ways that vouch for a more united India with an improved taxing landscape.
But before we get into the lens of administration, let’s take a closer look at the reasons behind the wide acceptance of GST!
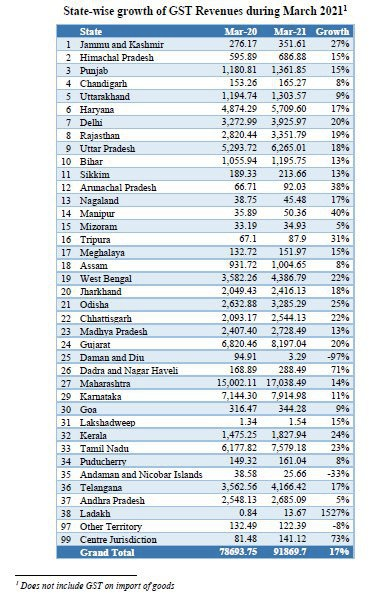 sample report that helps in identifying trends based on the GST data
The Indian government leverages GST data to ensure adherence to tax laws, streamline tax collection procedures, and identify potential instances of tax evasion. The reduction in manual errors has significantly enhanced the precision of tax assessments, facilitating proactive measures against tax fraud and enabling timely decision-making with the availability of real-time data.
Moreover, the application of advanced analytics and data mining techniques to GST data proves highly advantageous. It empowers tax authorities to discern noncompliance patterns, pinpoint high-risk taxpayers, and optimize audit selection.
Such a proactive approach not only safeguards government revenue but also fosters a fair and equitable tax system. The pivotal role of GST data in shaping modern tax administration supports economic growth and reinforces a robust fiscal framework.
sample report that helps in identifying trends based on the GST data
The Indian government leverages GST data to ensure adherence to tax laws, streamline tax collection procedures, and identify potential instances of tax evasion. The reduction in manual errors has significantly enhanced the precision of tax assessments, facilitating proactive measures against tax fraud and enabling timely decision-making with the availability of real-time data.
Moreover, the application of advanced analytics and data mining techniques to GST data proves highly advantageous. It empowers tax authorities to discern noncompliance patterns, pinpoint high-risk taxpayers, and optimize audit selection.
Such a proactive approach not only safeguards government revenue but also fosters a fair and equitable tax system. The pivotal role of GST data in shaping modern tax administration supports economic growth and reinforces a robust fiscal framework.
Reasons Behind The Success of GST
The Income Tax Department in India is a great source of information. Individuals and corporations file tax returns, which are augmented by information obtained from other sources such as credit card companies, banks, and more. This thorough data gathering goes beyond simple submissions. To find possible areas of interest, the spending habits of those who are engaged in high-value transactions requiring significant outlays are closely scrutinized. This examination probes the financial behavior of organizations involved in large-scale transactions and offers valuable insights into their economic behavior. Combining data from many sources improves the department’s ability to evaluate revenue and expenses precisely, which leads to a more comprehensive picture of the financial environment. The information provided is used by the property registrar to gather information about the parties to real estate transactions over a certain threshold. Advanced data analysis is made possible by every financial transaction connected to the PAN established with the tax department. Furthermore, information is obtained from a number of government agencies, such as the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, the Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN), and SEBI.
The roaring success of GST and the invaluable data provided by the system knows no bounds. It has helped tax administration in ways that vouch for a more united India with an improved taxing landscape.
But before we get into the lens of administration, let’s take a closer look at the reasons behind the wide acceptance of GST!
The information provided is used by the property registrar to gather information about the parties to real estate transactions over a certain threshold. Advanced data analysis is made possible by every financial transaction connected to the PAN established with the tax department. Furthermore, information is obtained from a number of government agencies, such as the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, the Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN), and SEBI.
The roaring success of GST and the invaluable data provided by the system knows no bounds. It has helped tax administration in ways that vouch for a more united India with an improved taxing landscape.
But before we get into the lens of administration, let’s take a closer look at the reasons behind the wide acceptance of GST!
-
Bidding Farewell To Multiple Taxes
-
Curbing Tax Evasion
-
Indirect Taxes Subsumed
-
Increasing Numbers of Taxpayers
-
Eliminating Cascading Taxes
-
Online Procedures
-
Increase Consumption
-
Efficient Logistics and Distribution System
How is GST Data Leveraged for Tax Administration?
Governments now possess a potent tool to enhance efficiency, transparency, and compliance, thanks to the transformative impact of utilizing GST data in tax administration. GST, being a consumption-centric tax, generates an extensive dataset of economic transactions, offering tax authorities crucial insights into the financial activities of businesses. sample report that helps in identifying trends based on the GST data
The Indian government leverages GST data to ensure adherence to tax laws, streamline tax collection procedures, and identify potential instances of tax evasion. The reduction in manual errors has significantly enhanced the precision of tax assessments, facilitating proactive measures against tax fraud and enabling timely decision-making with the availability of real-time data.
Moreover, the application of advanced analytics and data mining techniques to GST data proves highly advantageous. It empowers tax authorities to discern noncompliance patterns, pinpoint high-risk taxpayers, and optimize audit selection.
Such a proactive approach not only safeguards government revenue but also fosters a fair and equitable tax system. The pivotal role of GST data in shaping modern tax administration supports economic growth and reinforces a robust fiscal framework.
sample report that helps in identifying trends based on the GST data
The Indian government leverages GST data to ensure adherence to tax laws, streamline tax collection procedures, and identify potential instances of tax evasion. The reduction in manual errors has significantly enhanced the precision of tax assessments, facilitating proactive measures against tax fraud and enabling timely decision-making with the availability of real-time data.
Moreover, the application of advanced analytics and data mining techniques to GST data proves highly advantageous. It empowers tax authorities to discern noncompliance patterns, pinpoint high-risk taxpayers, and optimize audit selection.
Such a proactive approach not only safeguards government revenue but also fosters a fair and equitable tax system. The pivotal role of GST data in shaping modern tax administration supports economic growth and reinforces a robust fiscal framework.
Conclusion
Without a doubt, as India’s history unfolds in the coming years, the alterations brought about by GST will be recognized as catalysts propelling development and progress. These initial years signify a period of infancy, demanding further nurturing to facilitate the transformation of this system into a forward-thinking, amiable adult that contributes to the overall well-being of society. As the GST tax administration progresses and undergoes enhancements, it holds the potential to revolutionize Indian tax administration. It has already paved the way for a more efficient and transparent system, establishing itself as an essential component of the indirect tax landscape in India. With aspirations to function as a singular indirect tax system, supplanting various other taxes on goods and services, GST aims to make the overall system more effective and fruitful.Frequently Asked Questions
-
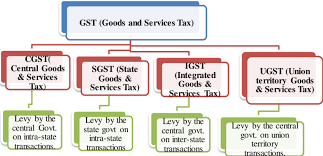
What kinds of GST are there?
-
What is the taxable event under GST?
-
Can I register for GST online?
-
What is the time limit for taking a registration under GST?
-
Whether the proper officer rejects an Application for Registration?
-
Whether the registration granted to any person is permanent?
-
Can the registration certificate be downloaded from the GSTN portal?
-
Which authority will levy and administer GST?
-
Who will decide the rates for the levy of GST?
-
Is there any fine for not filing a GST return on time?
Leverage GST data for smarter tax administration and simplify compliance with CaptainBiz.
Kiran Jagadale
I am a seasoned marketer specializing in Tax, Finance, and Digital. I bring a wealth of hands-on experience to demystify complex subjects, providing insightful guidance for entrepreneurs, finance enthusiasts, and digital marketers alike.
