Within the complex realm of business transactions, documentation assumes a critical role. Essential paper trails, such as invoices, receipts, and bills of lading, intricately facilitate the functioning of commerce. Among these, the bill of supply emerges as a unique instrument employed in scenarios where the standard tax invoice may not be suitable. A GST bill of supply plays a vital role in maintaining the seamless operation of businesses by ensuring adherence to tax regulations and creating a transparent record of exchanged goods and services.
What exactly is a bill of supply, and under what circumstances does it become relevant?
Meaning of bill of supply
- In the framework of the Goods and Services Tax (GST), a bill of supply serves as a substitute for a tax invoice.
- It is dispensed by registered businesses engaged in transactions involving exempted goods or services, as well as by composition vendors who lack the eligibility to levy taxes on their clientele. This document becomes obligatory in scenarios where a tax invoice is not mandated. For example, in the supply of exempted goods, business with unregistered dealers, or transactions involving non-taxable supplies.
- In India, entities registered under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime are required to furnish a bill of supply for such sales transactions.
Getting to know the GST bill of supply
A bill of supply can be considered as a special kind of receipt given by a business to its customers. This receipt shows what goods or services were provided and how much they cost. The unique thing about a bill of supply is that it doesn’t include any taxes.
There are two main situations where businesses use bills of supply:
Exempt Supplies
- Some businesses sell products or offer services that are not taxed under the Goods and Services Tax (GST).
- In these cases, instead of a regular receipt with taxes, they use a bill of supply.
- Examples of such untaxed items include basic food grains, educational services, and healthcare.
Composite suppliers
- Certain businesses, part of the GST composition scheme, don’t have to deal with taxes directly.
- For them, the bill of supply is like their main receipt for all transactions.
- They don’t charge or collect taxes separately.
- The bill of supply covers everything they sell.
Decoding the details of the GST Bill of Supply
While the fundamental purpose of a bill of supply remains the same, its specific structure and requirements can differ based on the type of GST registration and the nature of goods or services involved.
Regular GST-Registered Suppliers
- Businesses falling under this category need to ensure that their bill of supply includes specific essential details.
- These comprise information about the supplier and recipient, a description of the goods or services, quantity, value, HSN/SAC code, and a clear declaration stating “GST is not applicable.”
Composition Suppliers
- The bill of supply for businesses operating under the composition scheme follows a slightly different format.
- It should encompass details such as information about the supplier and recipient, a description of the goods or services, quantity, value, and a declaration confirming that the supplier is registered under the composition scheme.
Bill of Supply for small businesses and exporters
Be it a startup, small business, or an established export venture, a bill of supply holds significant importance for all business entities.
Bill of supply for small businesses
Simplified compliance
- Especially beneficial for small businesses dealing with exempt supplies, bills of supply offer a streamlined alternative to tax invoices.
- This eases the burden of paperwork and administrative tasks.
Maintaining transparency
- Even in case of exempt supplies, a well-structured bill of supply is essential.
- It ensures financial transactions are clear and transparent, fostering trust with customers and potential investors.
Bill of supply for exporters
Proof of export
- Bills of supply play a pivotal role in claiming duty drawback—a government incentive for exporters.
- Bill of supply for exporters acts as evidence that the goods were exported and not sold domestically, facilitating tax refunds.
Foreign trade documentation
- In foreign trade, bills of supply become crucial supporting documents.
They are vital for tasks such as customs clearance and applications for letters of credit, contributing to the smooth flow of export-related transactions.
Note:
Goods exported under GST are exempt from taxation. GST does not apply to foreign recipients of goods or services. Therefore, when exporting, the exporter can issue a bill of supply without referencing CGST, SGST, IGST, and Cess. Similar to the bill of export from a composition scheme dealer, the bill of supply from an exporter should include the following notations:
- “Supply Meant For Export On Payment Of IGST”
- “Supply Meant For Export Under Bond Or Letter Of Undertaking Without Payment Of IGST”
Contents of the bill of supply
A bill of supply is required to contain the following information (details)
| Details of the supplier | Name of the firm, address, contact number, GSTIN, |
| Details of the purchaser | Name of the firm, address, contact number, GSTIN (in case if registered) |
| Serial number | It must be generated consecutively, unique for each bill of supply in a particular financial year.
It should not exceed 16 characters. |
| Date | The date of issue of the bill of supply must be clearly specified. |
| Description of goods or services | A detailed description of the goods supplied or services offered must be given. |
| Code | For goods, the HSN code needs to be mentioned
For service, the accounting code needs to be mentioned. |
| Total value of the goods or services | The total value of the goods or services after adjusting any discount must be clearly specified |
| Declaration | The bill of supply must carry a declaration that it shows the actual price of the goods or services mentioned and that all details are correct and true. |
| Signature | The bill of supply should carry a signature or digital signature of the supplier |
| आपूर्तिकर्ता का विवरण | फर्म का नाम, पता, संपर्क नंबर, जीएसटीआईएन |
| क्रेता का विवरण | फर्म का नाम, पता, संपर्क नंबर, जीएसटीआईएन (पंजीकृत होने की स्थिति में) |
| क्रम संख्या | इसे किसी विशेष वित्तीय वर्ष में आपूर्ति के प्रत्येक बिल के लिए लगातार, अद्वितीय रूप से तैयार किया जाना चाहिए।
यह 16 अक्षरों से अधिक नहीं होना चाहिए. |
| तारीख | आपूर्ति बिल जारी करने की तारीख स्पष्ट रूप से निर्दिष्ट होनी चाहिए। |
| वस्तुओं या सेवाओं का विवरण | आपूर्ति की गई वस्तुओं या दी गई सेवाओं का विस्तृत विवरण दिया जाना चाहिए। |
| कोड | सामान के लिए एचएसएन कोड बताना जरूरी है
सेवा के लिए, लेखांकन कोड का उल्लेख करना आवश्यक है। |
| वस्तुओं या सेवाओं का कुल मूल्य | The total value of the goods or services after adjusting any discount must be clearly specified |
| घोषणा | आपूर्ति के बिल में एक घोषणा होनी चाहिए कि यह उल्लिखित वस्तुओं या सेवाओं की वास्तविक कीमत दर्शाता है और सभी विवरण सही और सत्य हैं। |
| हस्ताक्षर | आपूर्ति के बिल पर आपूर्तिकर्ता के हस्ताक्षर या डिजिटल हस्ताक्षर होने चाहिए। |
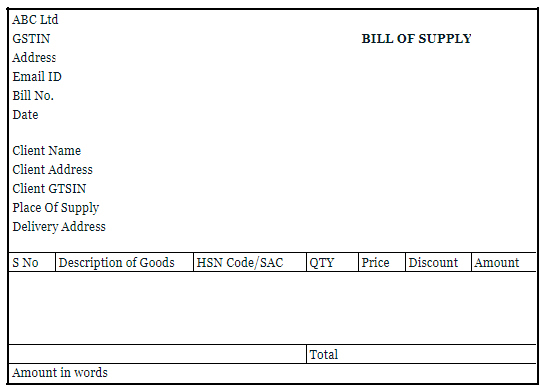
A Bill Of Supply Sample
Significance of Bill of Supply in the GST Framework
The bill of supply holds substantial importance for both suppliers and recipients of goods or services under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime. Here are the benefits of bill of supply:
GST compliance
- The bill of supply is an effective alternative for non-taxable Supplies.
- When a registered dealer is ineligible to collect GST on certain supplies, a bill of supply serves as the compliant alternative to a tax invoice.
- This ensures adherence to GST regulations, preventing penalties for non-compliance.
Streamlined tax return filing
- Businesses can simplify the process of filing their GST returns with a GST bill of supply.
- This ensures eligibility for claiming input tax credit by maintaining precise records of Bills of Supply.
Claiming the Input Tax Credit (ITC)
- For a registered dealer to claim Input Tax Credit, valid documentation is essential.
- The GST bill of supply is a valid document for ITC claims.
- In cases of exempt supplies or those under the Composition Scheme, the prescribed document is the Bill of Supply.
- Issuing this document becomes crucial for enabling recipients to claim ITC.
Increased credibility
- The issuance of a bill of supply not only serves as a regulatory requirement but also contributes to enhancing the credibility of the business.
- It fosters trust with customers, showcasing transparency and adherence to established procedures.
Record-keeping
- GST mandates dealers to maintain precise records of all transactions.
- Issuing a bill of supply facilitates proper record-keeping, particularly for exempt supplies or transactions under the composition scheme.
- This practice supports effective accounting and audit processes.
Avoiding hassles
- The bill of supply clearly mentions that no GST has been charged on the supply.
- This clarity helps prevent disputes between suppliers and recipients concerning the tax aspect of the transaction.
Ease for small businesses and composition dealers
- The bill of supply, being a straightforward document, is easy to issue and manage.
- This simplicity aids small businesses and composition dealers in complying with GST regulations, contributing to seamless business operations.
Tax Invoice vs Bill of Supply
Nature of Sales
- A Tax Invoice is utilized for all taxable sales, whether local or central.
- A Bill of Supply is used for exempt sales or sales by composition dealers.
Tax Details
- In a Tax Invoice, CGST, SGST, and IGST should be itemized separately.
- In a Bill of Supply, no taxes are displayed on the bill.
Requirements for unregistered buyers
- For a Tax Invoice, when the invoice value before taxes exceeds a certain limit, details such as name, address, state, and place of delivery are mandatory for unregistered buyers.
- A Bill of Supply does not require such information for unregistered buyers.
Applicability to local and central sales
- A Tax Invoice can be issued for both local and central sales.
- A Bill of Supply can only be issued for local sales in the case of a composition dealer.
The bill of supply might be easily overlooked, but it is really important in the business world. Even though it is not as well-known as the tax invoice, this document helps keep transactions transparent and ensures that businesses follow the complicated GST rules. Understanding why it is essential and the many benefits it brings gives business owners the tools they need to handle taxes and make their operations run more smoothly. Embracing the bill of supply isn’t just recognizing it; it is a smart move that helps businesses keep everything flowing smoothly. Whether dealing with GST rules or managing the supply chain, the bill of supply is a crucial piece that helps businesses stay accurate, follow rules, and make good decisions for long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What is a GST bill of supply?
A GST bill of supply is a paper given by a registered business person when selling goods or services that don’t have taxes, or when the seller is part of the composition scheme.
-
Who should issue a bill of supply?
A bill of supply should be given by a registered business person who sells tax-free goods or services, or by a business person in the composition scheme.
-
Can a business firm issue one bill of supply for many sales?
No, a business firm must give a separate bill of supply for each sale of goods or services, even if they are sold to the same person.
-
Is a GST bill of supply eligible for input tax credit?
No, a person getting a GST bill of supply can’t get credit for the taxes mentioned in the bill.
-
Can a bill of supply be used for both within a state and between states?
Yes, a bill of supply can be used for both within a state and between states when selling tax-free products or services.
-
What is the time limit for issuing a bill of supply?
A bill of supply must be given when selling goods or services, or before or when delivering products, whichever happens first.
-
Can a bill of supply be changed?
No, a bill of supply can’t be changed once it is issued.
-
What happens if a bill of supply is not given?
Not giving a GST bill of supply for qualified sales may lead to fines and not following GST rules.
-
Are there specific formats for a GST bill of supply?
There are no specific formats for a GST bill of supply. However, it must have all the necessary details according to GST laws.
-
What information should be present in a GST bill of supply?
Compulsory information in a bill of supply:
The GST law outlines specific details that must be included in a Bill of Supply:
Supplier’s Information
Name, address, and GSTIN (Goods and Services Tax Identification Number) of the supplier.
Bill of supply number
A unique bill of supply number generated consecutively, ensuring each bill has a distinct number for the corresponding financial year.
Recipient’s information (if registered)
If the recipient is a registered entity, the bill of supply should include their name, address, and GSTIN.
Product or service codes
HSN (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) Code for goods or an Accounting Code for services, specifying the classification of the supplied goods or services.