Introduction
The place of supply is the location of the recipient of goods, and determining it is a crucial aspect of modern commerce. It influences not only taxation but also regulatory compliance and logistical strategies in a business. In India, GST (Goods and Services Tax) is the taxation system that is followed across the nation.
According to GST, the place of supply is the location of the recipient of the goods or services. GST is a destination-based tax, which means that the state where the goods and services are consumed will be allowed to levy tax and not the state from which the supply was made.
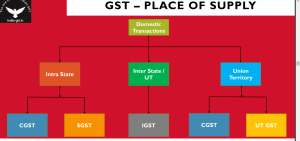
The place of supply determines the type of transaction, i.e., whether it is intra-state, inter-state, or import-export. This helps in determining which tax is to be applied, i.e., a combination of central (CGST) and state (SGST) taxes, or an integrated tax (IGST), with or without additional duties.
Thus, in this article, we will simplify how the place of supply is determined for goods, its importance, legal compliance, and much more.
https://icmai.in/upload/Taxation/IDT/PPT/GST-Place-Supply.pdf
Methodologies for determining the place of supply for goods
Determining the place of transaction has a great application in taxation, as we’ve already discussed earlier in the previous account. The methodologies that are involved in determining the place of supply for goods and services depend mainly upon three factors, i.e., the location of the supplier, recipient, and the movement of goods. Here we have a few key methodologies that help in establishing clarity in determining the place of supply for goods under the GST framework in India. This ensures that appropriate taxes are levied based on the nature and circumstances of the transaction.
-
Location of the Supplier and Recipient:
In this methodology, both the supplier and recipient are registered under GST, i.e., both have their own GSTIN (Goods and Services Tax Identification Number) details available. Here, the locations of both are known and the place of supply is the location of the recipient.
-
Location of the Goods at the Time of Delivery:
In this methodology, only the supplier is registered under GST, i.e., has a unique GSTIN and the recipient is not registered. Here, there is a movement of goods, but the location of the recipient is not available. So, the place of supply becomes the location where the goods are delivered.
-
Goods Delivered by the Supplier to a Recipient on the Direction of a Third Person:
In this case, the goods are supplied in the direction of a third person. Thus, the place of supply for the supplier is the location of the third person.
-
Import of Goods:
In this case, the place of supply for the supplier is the location of the importer, i.e., the location where the goods are first brought to India.
Also Read: How Is The Place Of Supply Determined For Goods?
Regulatory guidelines for accurate place-of-supply identification
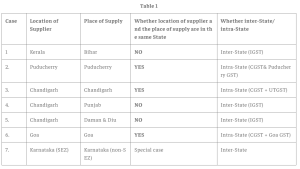
The regulatory guidelines for accurate place of supply identification are based on the location of the supplier, recipient, and specific transaction scenarios.
When it comes to GST, identification plays an important role in the correct application of taxes, as GST is a destination-based tax.
The place of supply determines whether a supply is intra-state (within the same state) or inter-state (across different states).
This, in turn, determines the applicable tax rate (CGST + SGST/UTGST for intra-state and IGST for inter-state).
https://www.taxmann.com/post/blog/place-of-supply-in-gst-with-examples/
Therefore, here are some guidelines to help you understand all of this in a simple manner:
-
Type of supply:
Consider the nature of the supply, whether it is interstate or intrastate. According to this nature, taxes are levied.
-
Interstate supply:
This is when goods are delivered from one state to another. The place of supply in this case is the destination state.
-
Intrastate supply:
Here, the goods are delivered in the same state; thus, the place of supply is in the same state.
-
Location of supplier and recipient:
Identify the location of the supplier and recipient, whether it is in India or not. It will help in levying taxes accordingly.
-
Invoicing and record-keeping:
Make sure that the invoice clearly mentions the place of supply as per the appropriate rules. For GST returns, one needs to make sure the place of supply is correctly reported in the GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B returns.
-
Compliance and Consequences of Incorrect Place of Supply Identification:
Errors in place of supply identification, incorrect place of supply, fraud, or deliberate misidentification may land you in a lot of trouble, like miscalculations and payment errors, penalty and interest charges, and criminal prosecution initiation, respectively.
Also Read: Understanding the Place of Supply Rules for Goods: A Comprehensive Guide
Compliance standards are in place for goods-related supply determinations
Compliance standards for goods-related supply determinations require accurately identifying the place of supply based on established rules. This in turn helps to correctly apply the applicable taxation and ensure adherence to regulatory requirements. Following these standards is crucial for businesses to ensure regulatory compliance, facilitate audits, and avoid penalties associated with non-compliance in the case of goods supply transactions. Here are some of the compliance standards:
-
Accuracy in Documentation:
Taxation requires the involvement of numerous documents, like invoices, transport-related documents, etc. These documents must be accurate to reflect the correct details of the supply transaction and, thus, the correct taxation protocols.
-
Timely Filing of Returns:
The process of taxation is very punctual. Thus, you need to maintain compliance with reporting requirements. One must adhere to the bound timelines for filing GST returns, including details of goods supplied.
-
Correct Application of GST Rates:
The GST rate application is based on the nature of the goods supplied. In addition, it considers the place of supply as well. The application is also based on the provisions of GST laws.
-
Verification of GSTIN and cooperation with tax authorities:
The GSTIN of both the supplier and recipient must be validated to ensure that only the registered entities are involved in the transaction. Cooperating with tax authorities is also crucial during audits, inspections, or inquiries related to goods supply transactions.
Strategies for efficient documentation of goods-related place of supply
Documentation is a pivotal part of taxation. Efficient documentation strategies for goods-related places of supply act as a helping hand for seamless taxation processes. These strategies are important for businesses and reduce the risk of penalties. You can involve Various strategies, like Training the staff, maintaining records, and seeking guidance from GST consultants, to enhance the efficiency of documentation. Some of these strategies are discussed below.
-
Clear Invoice Details:
Invoicing is the main documentation involved in taxation. Enhancing this with accurate details such as supplier and recipient GSTIN, description of goods, quantity, and value, providing a clear snapshot of the transaction, etc. will efficiently lead to improvement.
-
Accurate Place of Supply Mention:
The place of supply plays a major role in determining GST transactions. Thus, clearly specify the place of supply on invoices. While specifying, one must consider the nature of the transaction, whether it involves the movement of goods, import, or any other specific scenarios.
-
Comprehensive Record-Keeping:
It is important to keep a comprehensive record. This will be helpful for you in easy access during audits. You should follow the strategy to maintain a well-chronologically organized record, including invoices, delivery challans, and E-way bills, which are organized chronologically.
-
Automated Documentation Systems:
In this era of digitization, you can take help of IT and Implement automated systems for documentation. This will drastically reduce the manual errors and ensure consistency in recording the location of supply details across the transactions.
Also Read: Understanding GST Invoicing for Goods: Place of Supply Rules
Legal considerations in determining the place of supply for goods
In India, legal considerations involve adherence to provisions outlined in the Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST) Act, 2017, as well as relevant rules in the Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST) Act, 2017.
In addition, the State Goods and Services Tax (SGST) Acts, must be considered too. The place of supply must be determined with accurate documentation and stay informed about any updates or amendments issued by the GST Council. Here are some key legal aspects,
-
Location of Supplier and Recipient:
The GST laws in India for taxation make sure that the place of supply is dependent on both the supplier and the recipient. Inter and intra-state supply is also considered.
-
Movement of Goods:
Legal considerations of GST are here to define how the location of the recipient at the time of delivery impacts the taxation of supply.
-
Importation Rules:
As we already know, according to the legal provisions of GST, the location of the importer is the place of supply. This aspect aligns with international trade protocols and helps with smooth taxation.
-
Special cases- high-sea sales, stock transfers, a bill to ship to transactions:
These cases require special, careful consideration to determine the correct place of supply.
Maximizing benefits through precise identification of goods-related supply locations
Now that we know all about how the place of supply is determined, including the methodologies, benefits, and regulatory and legal compliance, it is time that we get to know how we can maximize this knowledge. This strategy of maximization will provide a seamless taxation process, minimize tax liabilities, etc. Thus, a few strategies for Maximizing benefits through precise identification of goods-related supply locations are as follows,
-
Input Tax Credit Optimization:
The input tax credit is optimally utilized when the place of supply is determined accurately. Thus, reducing tax liabilities and enhancing overall financial efficiency.
-
Compliance Efficiency:
When you determine the place of supply precisely, the risk of errors and penalties is reduced, and smooth audits are facilitated.
-
Enhanced Business Planning:
Place of supply identification will assist you in strategically planning operations, supply chain logistics, and pricing strategies, Thus, maximizing overall business efficiency.
Conclusion:
Therefore, we can conclude that the determination of the place of supply for goods is a crucial part of the taxation process. It holds a significant role for businesses and tax authorities alike. We can say that determining the correct place of supply is not just a compliance issue but a cornerstone for a business to maximize its efficiency both financially and ethically.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What is a place of supply?
The place of supply is the location of the recipient.
-
Is a place of supply important for business strategies?
Yes, it is important, as it will help you in legal compliance as well as financial efficiency.
-
How is the place of supply related to GST?
GST is a destination-based tax, i.e., tax will be levied at the location where the goods are consumed.
-
What are the types of places of supply based on location?
Interstate and intra-state.
-
What are interstate and intrastate places of supply?
Interstate- Supplier and recipient, both in the same state.
Intra-state- The supplier and recipient are both in different states.
-
In the case of importation, what is the place of supply?
The location of the importer is the place of supply.
-
Why is record keeping important?
Comprehensive record keeping is important, as it will be accessible at the time of audit.
-
Why is invoicing important?
A clear mention of the place of supply must be included in the invoice to ensure no miscalculations in taxation.
-
What is the role of the correct place of supply in compliance efficiency?
It will reduce errors and penalties and smooth audits will be facilitated.
-
What is the role of the correct place of supply in GST law application?
GST laws are applied based on the place of supply, as it is a destination-based law. It also helps determine which tax is to be applied, i.e., a combination of central (CGST) and state (SGST) taxes, or an integrated tax (IGST), with or without additional duties.
