Over 7.9 million Indian GST MSMEs existed on March 27, 2022, according to the Ministry of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises. About 30% of the nation’s manufacturing is MSMEs. Statista 2022 found 110 million Indians employed by MSME in 2016. Cities employ more MSME workers than rural areas.
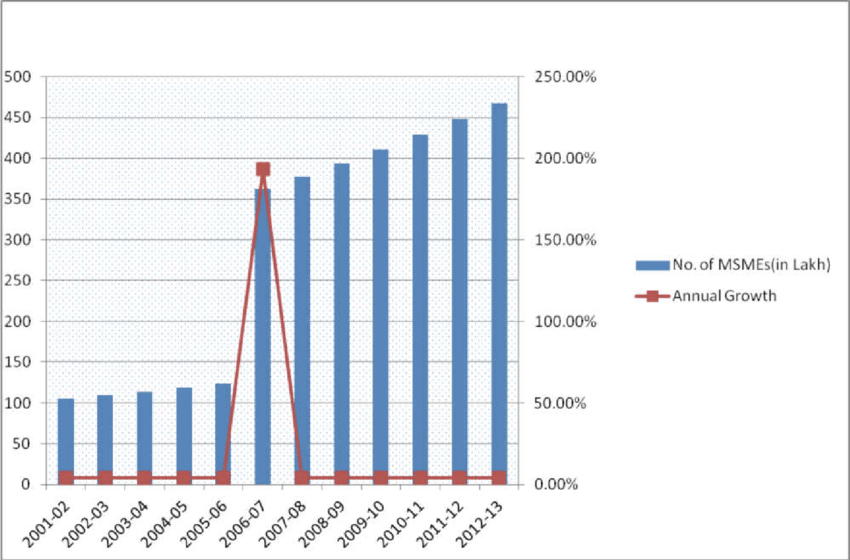
In the given period, tiny companies provide the most national employment. The biggest Indian backers are MSMEs. The Indian government introduced the GST Act on March 29, 2017, and it took effect on July 1, 2017, to help the industry. The government believed a unified market and workable tax framework would improve MSMEs’ operations.
Particular Billing Requirements for the MSME Industry
For taxpayers with a yearly revenue under ₹ 1.5 crore, the HSN code no longer needs to be mentioned in tax invoices. Taxpayers with annual turnovers between ₹ 1.5 Crore and ₹ 5 Crore can only include the first two digits of the HSN code in their invoices, while those with annual turnovers over ₹ 5 Crore must include the complete 4-digit number.
Special Provisions for MSME Sector Return Filing
The government has announced that, as a trade facilitation measure, all eligible registered persons with an annual turnover of up to ₹ 1.5 crore may choose to file a quarterly return within eighteen days of the end of the quarter in Form GSTR-1, which contains details of outward supplies of goods or services, or both, made during the quarter.
GST’s Benefits for The MSME Sector
The benefits and future goals of the GST Act are listed below:
- Indirect taxation would decrease in number.
- It doesn’t take long to produce the GST return because there are certain GST role in the MSME growth compliances.
- The GST registration procedure might be completed entirely online.
- It will be simpler to conduct interstate business through e-commerce operators after obtaining the GST registration.
- With the use of an online approach, GST MSME has regulated the unorganized business sector.
- A GSTIN may be used for all GST-related purposes once it has been assigned.
- In addition to lowering the tax liabilities and tax rates, GST provides a composition plan for filing taxes at a fixed rate.
- After compliance, you could just make an ITC claim.
- Discovering tax avoidance under GST registration is easier.
- The goal is to include more businesses in the GST’s purview. Consumption of goods and services would be driven.
- GST establishes fair costs for the goods or services.
Actions Made in Support of the MSME Sector In GST
The GST Council has made several decisions in its meetings that will help the MSME industry. The following are the specifics of these important decisions:
- Products that are primarily consumed and/or produced in the unorganized GST role in the MSME growth sector are either excluded or maintained at reduced rates. The tax rate on items such as electrical switches and wires, pipelines, plastic products, etc., which are mostly produced by MSMEs and do not pay central excise duty, has been reduced from 28% to 18%.
Similarly, the GST rates for goods created primarily in the cottage sector, such as handbags, ropes, and other items made of jute and coir, have been lowered from 12 to 5%. The percentage of fishing hooks, which are mostly utilized by fishermen in this labor-intensive sector with negligible ITC, has decreased from 12 to 5%.
- An increase of ₹ 1 Crore to ₹ 1.5 Crore will be the upper limit of turnover for choosing the composition plan.
- Permission to provide services to composition dealers. Service providers that have an annual revenue of up to ₹ 50 Lakh have the option to use a composition scheme; in this case, the appropriate GST rate is 6%.
- The GST Council recommends levying GST’s role in the MSME growth on reverse charge shipments from unregistered vendors. Only selected goods and registered persons will be affected by this process.
- If the recipient fails to pay the supplier within 180 days of the invoice’s issuance date, the input tax credit will be reimbursed.
MSMEs Are India’s Economic Foundation
MSMEs are, without a doubt, the foundation of the Indian economy. Hence, it is crucial to support their smooth operation. We frequently take its importance and effects on the Indian economy for granted.
Given the number of people operating small businesses and the job opportunities they present, the government supports these businesses and works to establish conditions that allow for their unrestricted operation through a variety of initiatives.
Implementing GST
The majority of the GST MSME sector has been credit-starved, and smaller businesses have made it economically inefficient. This industry has been severely damaged by the COVID-19 pandemic. Due to capital shortages, many people have lost their employment and cannot start new businesses. The GST was promptly imposed; however, many MSME enterprises are still tax-exempt. Without insightful data, policymakers struggle to create relevant and realistic responses.
Small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) are finding it difficult to comprehend and implement the new indirect tax regulations. Companies worry about having to follow complex registration requirements, convoluted refund regulations, and three returns to file each month.
SMBs will inevitably go digital, but the pace of digitization may be slowed by onerous GST requirements. Only the internet website may be used to finish the GST compliance process. Due to increased compliance expenses and a general lack of awareness about the newest technologies, small and medium-sized firms sometimes face more challenges.
GST Guidelines
SMBs are reluctant to register under the GST statute to avoid the laborious and inconvenient processes associated with registration and return filing—not to avoid paying taxes. This discourages MSMEs from investigating internet markets, which hinders India’s efforts to develop a digitally oriented economy.
The GST registration requirement for small online shops with less than Rs 40 lakh in turnover should be removed to create a balance between online and offline stores.
Nasscom argues that these sellers ought to be eligible for the composition scheme, which allows merchants and smaller companies to verify the authenticity of e-commerce operators’ warehouses in different states using just one physical location for company registration in the seller’s home state. These suggestions are relevant to the issues at hand, and if implemented, they will support the growth of Indian SMBs.
How Do MSMEs Handle Compliance with GST?
Local Circles contacted Indian entrepreneurs in early 2022 to get their opinions on how the GST affected their day-to-day operations. Survey results include:
- According to business taxes before the GST, 37% of businesses claimed GST compliance would take longer.
- 50% of businesses reported that since the GST was implemented, their monthly accounting expenses have increased.
- According to 75% of the enterprises, the primary problem with the GST will be input and output invoice matching. Just 45% of the enterprises reported having a positive experience with GST, whereas 24% reported having a negative experience.
- Issues with the business’s connection, delayed logging-in, and information submission are frequently observed on the GSTN website.
MSMEs’ Recommendations Regarding GST
Documents larger than MB cannot be uploaded to the portal; this restriction has to be lifted. The e-invoicing would only be valid for 24 hours; either this time limit could be extended, or the e-invoices could be sent to businesses automatically through email.
- If the revenue exceeds Rs. 10 crore, e-invoicing will be implemented. As of October 1, 2022, MSMEs are exempt from this requirement.
- Online GST registration is possible, but state GST authorities may do the physical verification. MSMEs should thus get in touch with the GST department employees who provide the anti-corruption measures.
- It is difficult to learn about the new registration that falls under federal or state authority. Regarding the information provided by their state jurisdiction office, newly registered taxpayers typically run into several misconceptions.
- The income tax department needs a separate tribunal since there are so many factual and legal questions. Petroleum goods are exempt from GST.
Government Tax Relief for Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises
The government recognizes the enormous contribution made by the MSME sector and is taking several measures to support its growth. This has given various GST roles in MSME growth-related compliances under the GST regime confidence. For example, the first exemption threshold of Rs. 20 lakhs has been raised to Rs. 40 lakhs for commodities.
The annual cap for the composition program was raised to Rs 1.5 cr for commodities and Rs 50 lakhs for services. The services could be rendered by those who deal with the composition.
The goal of GST is to increase the number of taxpayers, primarily MSME growth taxpayers, and this could burden them with compliance-related costs. However, over time, GST would increase the competitiveness of those same MSMEs by bringing them and big businesses into balance. The ability to compete with foreign competitors with low-cost manufacturing hubs such as Bangladesh, China, and the Philippines would be granted to MSMEs.
Conclusion
Without MSMEs’ involvement, it would not be possible for the digital economy to expand. Given that e-commerce can transform smaller firms through technology, the government ought to take action to reduce obstacles to compliance. The GST MSME sector has resulted in numerous milestones for the country due to its participation.
Thus, confusing tax laws must be removed to promote expansion in this vital industry. Small businesses find it very difficult to use these because they lack technical knowledge, and most tools and solutions are too expensive for them to use, even though the government has made it easier for businesses to connect to the GST infrastructure through APIs to speed up the process.
FAQs
-
How Important Are Msmes To The Indian Economy, And How Many Are There?
GST role in the MSME growth, with over 7.9 million firms as of March 27, 2022, boosts the Indian economy. They produce 30% of the nation’s manufactured commodities and provide jobs.
-
When Was The GST Act Passed, And What Was The Government’s Goal, Especially For Msmes?
GST was introduced on March 29, 2017, and implemented on July 1, 2017. The government sought a single market and a viable tax framework to improve MSMEs’ operating efficiency.
-
What Gst-Specific Invoicing Requirements Apply To Msme?
The HSN code on tax invoices is no longer necessary for taxpayers with an annual turnover of up to ₹1.5 crore. Under some conditions, HSN code inclusion depends on annual turnover.
-
How Has Gst Simplified Msmes’ Return Filing, And What Are Their Specific Provisions?
MSMEs with a turnover of ₹1.5 crore can file quarterly returns. File Form GSTR-1, outlining outbound supplies, within 18 days of the quarter’s conclusion.
-
How GST Has Improved Indirect Taxation For MSME Sector. What Are Its Benefits?
GST has cut indirect taxes, simplified compliance, allowed online registration, and facilitated interstate business for MSMEs. It tries to increase business participation and consumption.
-
What GST Council Decisions Have Supported Msme?
The GST Council has reduced tax rates on MSMEs’ main products, raised the composition scheme’s maximum limit, allowed composition dealer services, and adjusted the reverse charge system.
-
What Problems Have Msmes Faced With GST in Their Daily Operations?
A survey found that the GST role in the MSME growth compliance takes time and that 50% of businesses’ monthly accounting expenses have grown since its adoption. The main issues include input and output invoice matching.
-
What GST Compliance Changes Do Msmes Suggest?
MSMEs advocate lowering portal upload document size restrictions, extending e-invoicing validity, and simplifying registration. They also advise exempting small internet shops from GST registration.
-
What Exemption Thresholds And Composition Scheme Caps Have The Government Changed For Smes Receiving Tax Relief?
The composition scheme’s yearly maximum has been lifted, and the government intends to make the GST role in the MSME growth more competitive by raising the exemption level for commodities to Rs. 40 lakhs.
-
How Can MSMEs Contribute To The Digital Economy, And How Can The Government Help Them Expand Through GST Compliance?
MSMEs are key to digital economy growth. The government should reduce compliance barriers, especially technology-related ones, to boost these vital firms.