Introduction of GST in India marked a transformative shift in the country’s tax structure, amalgamating multiple indirect taxes into a unified framework. This significant change has been a subject of extensive discussion, analysis, and sometimes, confusion among the business owners and stakeholders. The GST regime, by design, aims to enhance the ease of doing business and streamline the tax compliance process across the nation.
For business owners, GST invoices are more than just a document for record-keeping. They serve as the backbone of the GST invoice requirements, enabling the seamless flow of input tax credit across the supply chain, from manufacturers to end consumers. This guide aims to shed light on the essential aspects of GST invoicing, including the invoice format compliance, GST billing regulations, and the role of technology in streamlining the process.
Key Components of a GST Invoice
| Component | Description |
| GSTIN of the Supplier | The GST Identification Number of the supplier. |
| Name and Address of the Supplier | The complete address and name of the supplier issuing the invoice. |
| GSTIN of the Recipient | The GST Identification Number of the recipient (if registered under GST). |
| Name and Address of the Recipient | The complete address and name of the recipient. |
| Invoice Number | A unique serial number for the invoice, not exceeding 16 characters. |
| Invoice Date | The date when the invoice was issued. |
| Description of Goods or Services | A detailed description of the goods or services supplied. |
| HSN/SAC Codes | Harmonized System of Nomenclature code for goods or Service Accounting Codes for services. |
| Quantity of Goods or Services | The quantity of the goods supplied or the tenure/extent of the services provided. |
| Taxable Value | The value of the goods or services that are taxable. |
| Rate of Tax (CGST, SGST/UTGST, IGST) | The applicable GST rates for CGST, SGST/UTGST, and IGST. |
| Tax Amount (CGST, SGST/UTGST, IGST) | The total tax amount charged, shown separately for CGST, SGST/UTGST, and IGST. |
| Place of Supply | The location of the recipient where the goods are delivered or the services are provided. |
| Signature of the Supplier | The supplier’s signature or digital signature. |
Among the most important documents involved in the Goods and Services Tax system, the GST invoice is vital for both the supplier and the consumer. It’s necessary for tax calculations and compliance, and it’s more than just a formality; it’s a detailed record of the purchases and sales. An accurate and complete GST invoice must contain the following elements:
-
GST Invoice Requirements:
- GSTIN of the Supplier: The GST Identification Number is a must-have to establish the authenticity and tax compliance of the business entity.
- Name and Address of the Supplier: Essential for identifying the origin of the invoice.
- GSTIN of the Recipient: Critical for businesses, as it enables the recipient to claim Input Tax Credit (ITC).
- Name and Address of the Recipient: Necessary for delivery and billing purposes.
- Invoice Number and Date: Unique identification for every transaction, ensuring easy tracking and reference over time.
- Description of Goods/Services: A clear description helps in identifying the nature of goods or services involved in the transaction.
- HSN/SAC Codes: Harmonized System of Nomenclature for goods or Service Accounting Code for services is required for classification and tax purposes.
- Quantity of Goods: The measure or number of goods supplied is essential for inventory and accounting.
- Taxable Value: The value of goods or services that is subject to tax.
- Rate of Tax: The applicable GST rate(s) (CGST, SGST/UTGST, IGST, and cess if any).
- Tax Amount: The total tax charged, showing the CGST, SGST/UTGST, IGST, and cess separately.
- Place of Supply: Especially important in determining the nature of tax applicable (CGST + SGST/UTGST or IGST).
- Signature of the Supplier: A mandatory component that authenticates the invoice.
-
Invoice Format Compliance:
Ensuring the invoice adheres to the prescribed GST format is crucial for legality and facilitates the seamless claiming of Input Tax Credit (ITC). Non-compliance can lead to disputes, penalties, and denial of ITC.
Also Read: Tax Invoice Format for Meeting Compliance Standards
-
Tax Invoice Essentials:
Accurately reflecting the tax charged on the invoice is non-negotiable. It involves detailing the separate components of GST applicable, enabling clear tax computation and compliance.
-
Additional Details:
- Reverse Charge Indicator: If applicable, it should be mentioned that tax is payable on a reverse charge basis.
- Delivery Address: If it’s different from the billing address, it must be included, especially for physical goods.
- Reference Number: If the invoice relates to a Purchase Order or an agreement, referencing it can simplify reconciliation processes.
- Discounts: If any discounts are given before the calculation of the taxable value, these should be mentioned.
- Terms of Delivery: Including payment terms, delivery method, etc., provides clarity on the agreement between the supplier and the recipient.
Assuring compliance with GST legislation and facilitating a seamless and transparent business operation are both achieved by including all these components in a GST invoice. As a result, fewer disputes and penalties are accrued, and taxpayers are able to claim ITC correctly.
Understanding GST Invoice Rules
The GST framework specifies clear rules for invoicing, including when and how invoices should be issued:
- Invoice Number Guidelines: The invoice number should be unique and not exceed 16 characters, ensuring easy tracking and reference.
- GST Billing Regulations: These regulations outline the timing and conditions under which an invoice should be issued, depending on the nature of the supply (goods or services) and the specific circumstances of the sale or service delivery.
In order to simplify their billing procedures and stay in compliance, businesses must understand the subtleties of GST invoicing requirements. There are a number of important requirements that govern the invoicing process under the GST regime, in addition to the criteria for invoice numbers and GST billing regulations. Companies should also be aware of the following regulations:
-
Sequential Invoice Numbering
Invoices should be sequentially numbered for each financial year. This ensures that every invoice can be uniquely identified and tracked.
-
Tax Invoice Issuance Time Frame
- For goods, the invoice must be issued at the time of supply of goods for delivery or at the time of delivery to the recipient.
- For services, the invoice needs to be issued within 30 days of the service delivery. For banks and financial institutions, this period is extended to 45 days.
-
Duplicate and Triplicate Copies
- For the supply of goods, three copies of the invoice should be issued – the original for the recipient, a duplicate for the transporter, and a triplicate for the supplier.
- For the supply of services, two copies should be issued – the original for the recipient and a duplicate for the service provider.
-
Invoice for Exports
Invoices for goods or services exported out of India must contain a declaration that the supply is meant for export, along with the relevant shipping bill or bill of export details.
-
Revised Invoices
Businesses registered under GST can issue updated invoices for supplies made between the effective date of registration and the registration certificate date. These invoices must be issued within one month from the date of registration.
-
Bill of Supply
A bill of supply must be issued instead of a tax invoice by registered persons supplying exempted goods or services, or if they are enrolled under the GST composition scheme.
-
Credit and Debit Notes
When adjustments are required to be made after a tax invoice has been issued, businesses must issue credit or debit notes to reflect any increases or decreases in the invoice value.
-
Digital Signatures
Invoices can be authenticated using a digital signature to ensure the security and authenticity of the electronic documents being issued.
-
E-Invoicing
For businesses with a turnover exceeding a certain threshold, e-invoicing is mandatory. This involves the generation of invoices on a centralised government portal which assigns a unique identification number to each invoice.
-
Advance Payments
If an advance payment is received for a supply, a receipt voucher must be issued. If the supply is not subsequently made, a refund voucher should be issued against the advance received.
The purpose of these regulations is to guarantee transparency, traceability, and adherence to the GST system. By following these GST billing regulations, firms can prevent penalties and streamline tax administration and credit mechanisms.
GST Invoice Formats
Although there is no standardised structure for a GST invoice, it is crucial to follow format requirements to ensure its legitimacy. The invoice should include all tax invoice essentials, including GSTIN, invoice number, date, supply details, HSN/SAC codes, tax rates, and amounts, among other necessary facts. Businesses can significantly reduce the cost of compliance by utilising standardised software or templates, which guarantee that all invoices consistently include the required elements.
Here is a template for your reference to get started:
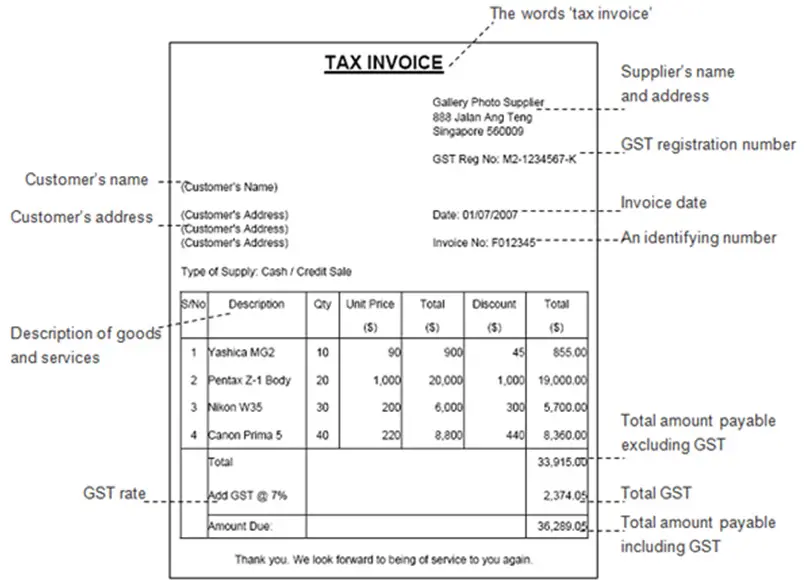
Also Read: Revolutionize Your Invoices: Creative Bill Formats In Word And Excel
Compliance and Legal Aspects
Maintaining compliance with the laws governing GST invoicing is not only about adhering to the law; it is also about ensuring that corporate operations run smoothly. Failure to comply with GST regulations can result in the rejection of ITC claims, penalties, and potentially the loss of business. It is essential for all firms that are registered for GST to have a thorough understanding of the legal requirements and to make certain that all invoices comply with these standards.
Role of Technology in GST Invoicing
Technology plays a pivotal role in GST compliance, offering solutions that automate and simplify invoicing processes. From generating compliant invoices to filing GST returns, technology can help businesses save time, reduce errors, and improve efficiency. Here’s how technology helps in the process:
- Automation of Invoice Creation: Technology automates GST-compliant invoice generation, reducing manual data entry and errors. This automation assures invoices include GSTIN, HSN/SAC codes, and tax calculations.
- Seamless Integration with Accounting Systems: Advanced software solutions provide real-time transaction tracking by integrating with existing accounting and ERP systems. This interface synchronises financial data across the organisation, enabling accurate and timely GST filings.
- E-Invoicing and Real-Time Reporting: GST requires firms with a specific turnover threshold to generate and submit electronic invoices. E-invoicing is supported by technology that lets firms create GST-compliant invoices. This streamlines invoice administration and allows real-time tracking and reporting.
Best Practices for GST Invoicing
To ensure compliance and optimise the GST invoicing process, businesses should adopt best practices such as:
- Regularly updating invoice templates to comply with changes in GST laws.
- Using GST-compliant accounting software.
- Keeping accurate records of all transactions.
- Educating the team about GST invoicing requirements.
Also Read: GST Invoicing Best Practices For Indian Businesses
Conclusion
It is essential for every business to stay informed about the requirements for GST invoices in order to function efficiently and remain in accordance with tax regulations. To ensure compliance and avoid issues with tax authorities, businesses should diligently adhere to the tax invoice essentials, ensuring accuracy and adherence. This will facilitate seamless operation of their firm. Utilising technology proficiently can significantly enhance efficiency throughout the entire procedure.
Also Listen: Process of Creating Purchase Orders and Invoices With CaptainBiz -Tutorials
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What are the basic GST Invoice Requirements?
Every GST invoice must include GSTIN, supplier and recipient details, invoice number and date, HSN/SAC codes, taxable value, tax amount, and a description of goods/services.
-
How does Invoice Format Compliance impact GST filing?
Proper invoice format compliance ensures smooth GST filing and claiming of Input Tax Credit. It minimises errors and discrepancies during tax audits and assessments.
-
What are the key GST Billing Regulations for services?
Services require invoices within 30 days of completion. They must detail the service, rate, tax, and place of supply to comply with GST regulations.
-
Why are Invoice Number Guidelines important in GST?
Invoice number guidelines ensure each transaction is uniquely identifiable, aiding in accurate record-keeping, tax calculation, and compliance with GST laws.
-
Can I issue a handwritten GST invoice?
Yes, but it must meet all Tax Invoice Essentials, including GSTIN, dates, details of supply, and tax calculated, ensuring it’s compliant for audit purposes.
-
What happens if my GST invoice is not compliant?
Non-compliant invoices can lead to denied Input Tax Credit claims, penalties, and potential legal action for not adhering to GST Invoice Requirements.
-
Is digital signature mandatory for GST invoicing?
Digital signatures are encouraged for authenticity and security, aligning with Invoice Format Compliance, but physical signatures are also accepted.
-
How do I rectify a mistake in a GST invoice?
Issue a credit or debit note with corrected details to align with GST Billing Regulations, ensuring both documents reference each other for clarity.
-
Are there special GST Invoice Requirements for exports?
Yes, export invoices must specify “Supply Meant for Export” and include shipping bill details, adhering to specific GST Billing Regulations for exports.
-
How often should I review my GST invoicing process?
Regular reviews ensure ongoing compliance with GST Invoice Requirements, adapting to any changes in GST Billing Regulations, formats, or tax laws.
