Common Registration involves multiple entities registering together, while Separate Registrations mean each entity registers individually. The key difference lies in centralized versus individual registrations. To decide, businesses must assess factors like their structure, autonomy needs, and operational interdependence. This choice significantly impacts tax liability and compliance. This discussion aims to provide a clear understanding of both approaches, aiding businesses in making informed decisions tailored to their specific needs.
Common NRT GST Registration vs. Separate Registrations

| Aspect | Common NRT GST Registration | Separate NRT GST Registrations |
| Nature of Registration | Single registration for multiple entities | Individual registrations for each entity |
| Administrative Complexity | Reduced administrative burden as there’s one registration to manage | Higher administrative workload due to multiple registrations |
| Autonomy of Entities | Limited autonomy for individual entities | Each entity maintains autonomy in tax affairs |
| Risk Management | Risk of issues in one entity affecting the entire group | Issues in one entity do not directly impact others, providing risk isolation |
| Compliance Simplification | Streamlined compliance activities | Compliance may be more complex and duplicated across entities |
| Operational Flexibility | Less flexibility for individual entities in managing tax affairs | More flexibility for each entity in managing its tax affairs |
| Ease of Coordination | Easier coordination due to centralized registration | Coordination may be more challenging with decentralized registrations |
| Customization for Entities | Limited customization for individual entities | Each entity can customize its registration based on specific needs |
| Impact on Tax Liability | Collective tax liability for the group | Individual tax liability for each entity |
| Adaptability to Business Changes | May require re-registration in case of changes in business structure | More adaptable to changes in individual entities without affecting others |
This table provides a concise overview of the distinctions between Common NRT GST Registration and Separate NRT GST Registrations across various aspects.
Advantages and disadvantages of common NRT GST registration
| Aspect | Advantages of Common NRT GST Registration | Disadvantages of Common NRT GST Registration |
| Simplified Administration | – Reduced administrative burden as there’s only one registration to manage | – Limited autonomy for individual entities in managing their tax affairs |
| Streamlined Compliance | – Streamlined compliance activities with a centralized approach | – Risk of issues in one entity affecting the entire group |
| Centralized Reporting | – Unified reporting, making it easier to track and manage tax activities | – Potential for delays and complications if issues arise in the group |
| Operational Coordination | – Easier coordination and communication within the group | – Less flexibility for individual entities in adapting to changing needs |
| Risk Pooling | – Risk sharing among entities within the group, providing stability | – Contamination of issues, where problems in one entity affect the others |
This table summarizes the advantages and disadvantages of opting for Common NRT GST Registration. It highlights the benefits of simplified administration, streamlined compliance, and centralized reporting, while also acknowledging the challenges related to limited autonomy, potential risks, and the need for operational flexibility.
Benefits and drawbacks of separate NRT GST registrations
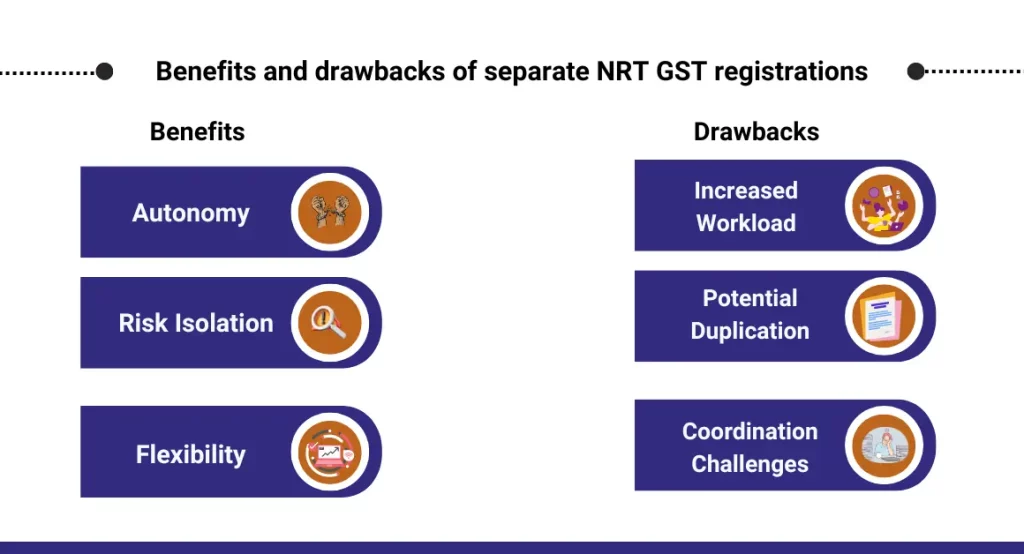
| Benefits of Separate NRT GST Registrations | Drawbacks of Separate NRT GST Registrations |
| – Autonomy: Entities maintain autonomy in managing tax affairs independently. | – Increased Administrative Workload: Managing multiple registrations can lead to higher administrative burden. |
| – Risk Isolation: Issues in one entity do not directly impact others, providing risk isolation. | – Potential Duplication: Some administrative tasks might be duplicated across entities, leading to inefficiencies. |
| – Flexibility: More flexibility for each entity to adapt registration based on specific business needs. | – Coordination Challenges: Coordination and communication between entities may become more challenging compared to a centralized registration approach. |
Factors to consider when choosing between common and separate registrations
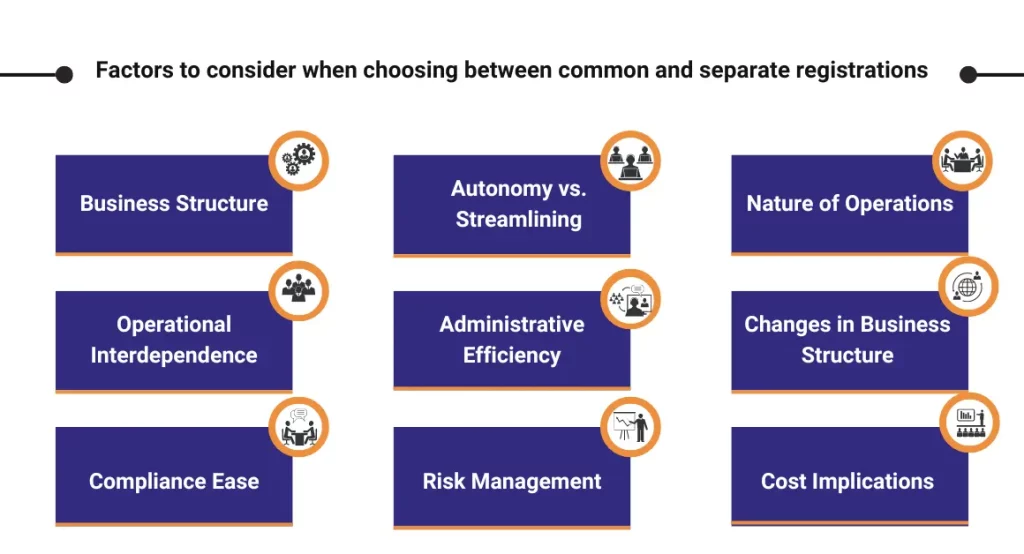
When deciding between Common and Separate NRT GST Registrations, several factors should be considered. Here are the key factors:
- Business Structure:
Consider the overall structure of the business, including the number of entities, their interdependence, and the hierarchy within the organization.
- Operational Interdependence:
Evaluate the level of operational interdependence between entities. If they operate independently, separate registrations may be more suitable.
- Compliance Ease:
Assess the ease of compliance with each approach. Common registration may simplify compliance, while separate registrations offer autonomy.
- Autonomy vs. Streamlining:
Balance the need for autonomy of individual entities with the advantages of streamlined processes under a common registration.
- Administrative Efficiency:
Consider the administrative efficiency of each approach. Common registration may reduce administrative complexities, but separate registrations offer more control.
- Risk Management:
Evaluate how each approach addresses risk. Common registration may expose the entire group to risks in one entity, while separate registrations can isolate risks.
- Nature of Operations:
Analyze the nature of business operations. If entities have distinct operations, separate registrations may align better with their unique requirements.
- Changes in Business Structure:
Consider the adaptability of the chosen approach to changes in the business structure, such as mergers, acquisitions, or divestitures.
- Cost Implications:
Evaluate the cost implications associated with both common and separate registrations, including initial setup costs and ongoing administrative expenses.
- Legal and Regulatory Considerations:
Ensure compliance with legal and regulatory requirements in the jurisdictions where the business operates, as these may impact the choice of registration.
Impact of registration choice on tax liability and compliance
The choice between Common and Separate NRT GST Registrations can significantly impact both tax liability and compliance. Here’s how:
Impact on Tax Liability:
-
Common NRT GST Registration:
Collective Tax Liability: Entities operating under a common registration share a collective tax liability. This means that the total tax liability is calculated for the entire group.
Risk Sharing: The tax burden is distributed among the entities, providing a degree of risk sharing. However, issues in one entity can affect the overall tax liability of the entire group.
Consolidated Reporting: Reporting is consolidated, making it easier to track and manage the overall tax position of the group.
-
Separate NRT GST Registrations:
Individual Tax Liability: Each entity maintains its individual tax liability. This offers autonomy but also means that the tax burden is specific to each entity.
Risk Isolation: Issues in one entity do not directly impact the tax liability of others. Each entity is responsible for its own tax position.
Individual Reporting: Reporting is done individually for each entity, which may require more effort to consolidate and analyze.
Impact on Compliance:
-
Common NRT GST Registration:
Streamlined Compliance: Compliance activities, such as filing returns and meeting regulatory requirements, can be more streamlined due to a centralized approach.
Unified Processes: Common registration often involves unified processes, which can simplify compliance activities for the entire group.
Risk of Contamination: However, issues in one entity may lead to complications for the entire group, impacting compliance across the board.
-
Separate NRT GST Registrations:
Autonomous Compliance: Each entity has autonomy in managing its compliance activities, tailoring them to its specific needs.
Increased Administration: However, managing compliance for multiple registrations can lead to increased administrative workload and potential duplication of efforts.
Customized Compliance: Compliance processes can be customized for each entity, but coordination may be more challenging.
In summary, the choice of registration has implications for how tax liability is calculated, shared, and reported, as well as how compliance activities are managed. Businesses need to carefully weigh these factors based on their operational structure, goals, and regulatory environment to make an informed decision.
Tailoring NRT GST registration strategy to business needs
Tailoring Non-Resident Tax (NRT) GST registration strategy to business needs involves a thoughtful consideration of various factors. Here are steps and considerations to help customize the strategy:
- Understand Business Structure:
Analyze the structure of the business, including the number of entities, their roles, and interdependencies. This understanding forms the basis for choosing a registration approach.
- Assess Operational Dynamics:
Evaluate how different entities within the business interact operationally. Consider whether they operate independently or share resources and functions.
- Identify Compliance Requirements:
Determine the specific compliance requirements for each entity. Some entities may have unique regulatory obligations that need to be addressed in the registration strategy.
- Consider Autonomy vs. Centralization:
Balance the need for autonomy of individual entities with the advantages of centralized processes. Determine the level of control each entity requires over its tax affairs.
- Evaluate Risk Tolerance:
Assess the business’s risk tolerance. If risk mitigation and isolation are crucial, separate registrations might be preferred to avoid the contamination of issues across entities.
- Review Tax Liability Implications:
Understand how the choice of registration impacts tax liability. Consider whether a collective tax liability or individual tax liabilities align better with the business’s financial goals.
- Adapt to Changes in Business Structure:
Design the registration strategy to be adaptable to changes in the business structure, such as mergers, acquisitions, or divestitures. Ensure that the strategy can evolve with the business.
- Evaluate Administrative Efficiencies:
Consider the administrative efficiencies associated with each approach. Assess whether a common registration streamlines processes or if separate registrations provide more flexibility.
- Customize Reporting and Communication:
Tailor reporting mechanisms to meet the specific needs of the business. Ensure that communication channels are effective, whether reporting is centralized or decentralized.
- Consider Industry Regulations:
Be aware of industry-specific regulations that may influence the registration strategy. Some industries may have unique compliance requirements that need to be integrated into the approach.
- Assess Cost Implications:
Evaluate the cost implications of both common and separate registrations. Consider initial setup costs, ongoing administrative expenses, and potential cost savings.
- Seek Professional Advice:
Consult with tax experts or legal advisors to gain insights into the regulatory landscape and receive tailored advice based on the specific needs of the business.
By systematically considering these factors, businesses can develop a Non-Resident Tax GST registration strategy that aligns with their unique requirements, operational dynamics, and long-term goals. Regular reviews and adjustments may be necessary to ensure continued alignment with evolving business needs.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, choosing between common and separate registrations involves weighing the advantages and disadvantages, considering factors like business structure and operational dynamics, and tailoring the strategy to meet specific business needs. The decision significantly impacts tax liability, compliance, and overall efficiency, making it crucial for businesses to carefully evaluate their unique circumstances before making a choice.
Also Read: GST: Everything You Need To Know
FAQ’s
-
What is the difference between Common NRT GST registration and Separate Registrations?
Common NRT GST registration involves registering multiple entities under a single registration, while separate registrations mean each entity registers individually.
-
What are the advantages of Common NRT GST registration?
Common registration streamlines administration, simplifies compliance, and provides unified reporting for multiple entities.
-
What are the disadvantages of Common NRT GST registration?
Common registration may limit the autonomy of individual entities, and issues in one entity can impact the entire group.
-
What are the benefits of Separate NRT GST registrations?
Separate registrations offer autonomy to individual entities, risk isolation, and flexibility in managing tax affairs according to specific needs.
-
What are the drawbacks of Separate NRT GST registrations?
Separate registrations may lead to increased administrative workload, potential duplication of tasks, and coordination challenges between entities.
-
What factors should businesses consider when choosing between Common and Separate NRT GST registrations?
Considerations include business structure, operational interdependence, compliance ease, autonomy, administrative efficiency, risk management, and more.
-
How does the choice of registration impact tax liability?
Common registration results in collective tax liability for the group, while separate registrations mean individual entities maintain their tax liabilities.
-
How does the choice of registration impact compliance?
Common registration streamlines compliance but may lead to complications if issues arise. Separate registrations offer autonomy but may involve increased administrative efforts.
-
How can businesses tailor NRT GST registration strategy to their needs?
By understanding business structure, assessing operational dynamics, considering autonomy, evaluating risk tolerance, adapting to changes, and seeking professional advice.
-
What is the importance of industry regulations in tailoring a registration strategy?
Industry regulations influence compliance requirements. Considering these regulations helps customize the registration strategy to meet specific industry standards.
