Common Registration involves multiple entities registering together, while Separate Registrations mean each entity registers individually. The key difference lies in centralized versus individual registrations. To decide, businesses must assess factors like their structure, autonomy needs, and operational interdependence. This choice significantly impacts tax liability and compliance. This discussion aims to provide a clear understanding of both approaches, aiding businesses in making informed decisions tailored to their specific needs.

This table provides a concise overview of the distinctions between Common NRT GST Registration and Separate NRT GST Registrations across various aspects.
This table summarizes the advantages and disadvantages of opting for Common NRT GST Registration. It highlights the benefits of simplified administration, streamlined compliance, and centralized reporting, while also acknowledging the challenges related to limited autonomy, potential risks, and the need for operational flexibility.
 When deciding between Common and Separate NRT GST Registrations, several factors should be considered. Here are the key factors:
When deciding between Common and Separate NRT GST Registrations, several factors should be considered. Here are the key factors:
Common NRT GST Registration vs. Separate Registrations

| Aspect | Common NRT GST Registration | Separate NRT GST Registrations |
| Nature of Registration | Single registration for multiple entities | Individual registrations for each entity |
| Administrative Complexity | Reduced administrative burden as there’s one registration to manage | Higher administrative workload due to multiple registrations |
| Autonomy of Entities | Limited autonomy for individual entities | Each entity maintains autonomy in tax affairs |
| Risk Management | Risk of issues in one entity affecting the entire group | Issues in one entity do not directly impact others, providing risk isolation |
| Compliance Simplification | Streamlined compliance activities | Compliance may be more complex and duplicated across entities |
| Operational Flexibility | Less flexibility for individual entities in managing tax affairs | More flexibility for each entity in managing its tax affairs |
| Ease of Coordination | Easier coordination due to centralized registration | Coordination may be more challenging with decentralized registrations |
| Customization for Entities | Limited customization for individual entities | Each entity can customize its registration based on specific needs |
| Impact on Tax Liability | Collective tax liability for the group | Individual tax liability for each entity |
| Adaptability to Business Changes | May require re-registration in case of changes in business structure | More adaptable to changes in individual entities without affecting others |
Advantages and disadvantages of common NRT GST registration
| Aspect | Advantages of Common NRT GST Registration | Disadvantages of Common NRT GST Registration |
| Simplified Administration | – Reduced administrative burden as there’s only one registration to manage | – Limited autonomy for individual entities in managing their tax affairs |
| Streamlined Compliance | – Streamlined compliance activities with a centralized approach | – Risk of issues in one entity affecting the entire group |
| Centralized Reporting | – Unified reporting, making it easier to track and manage tax activities | – Potential for delays and complications if issues arise in the group |
| Operational Coordination | – Easier coordination and communication within the group | – Less flexibility for individual entities in adapting to changing needs |
| Risk Pooling | – Risk sharing among entities within the group, providing stability | – Contamination of issues, where problems in one entity affect the others |
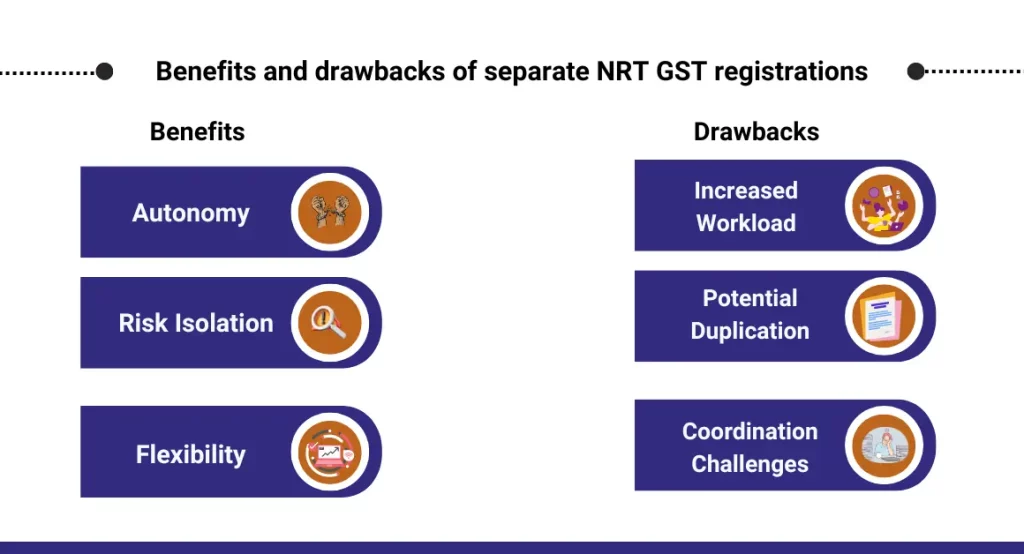
Benefits and drawbacks of separate NRT GST registrations

| Benefits of Separate NRT GST Registrations | Drawbacks of Separate NRT GST Registrations |
| – Autonomy: Entities maintain autonomy in managing tax affairs independently. | – Increased Administrative Workload: Managing multiple registrations can lead to higher administrative burden. |
| – Risk Isolation: Issues in one entity do not directly impact others, providing risk isolation. | – Potential Duplication: Some administrative tasks might be duplicated across entities, leading to inefficiencies. |
| – Flexibility: More flexibility for each entity to adapt registration based on specific business needs. | – Coordination Challenges: Coordination and communication between entities may become more challenging compared to a centralized registration approach. |
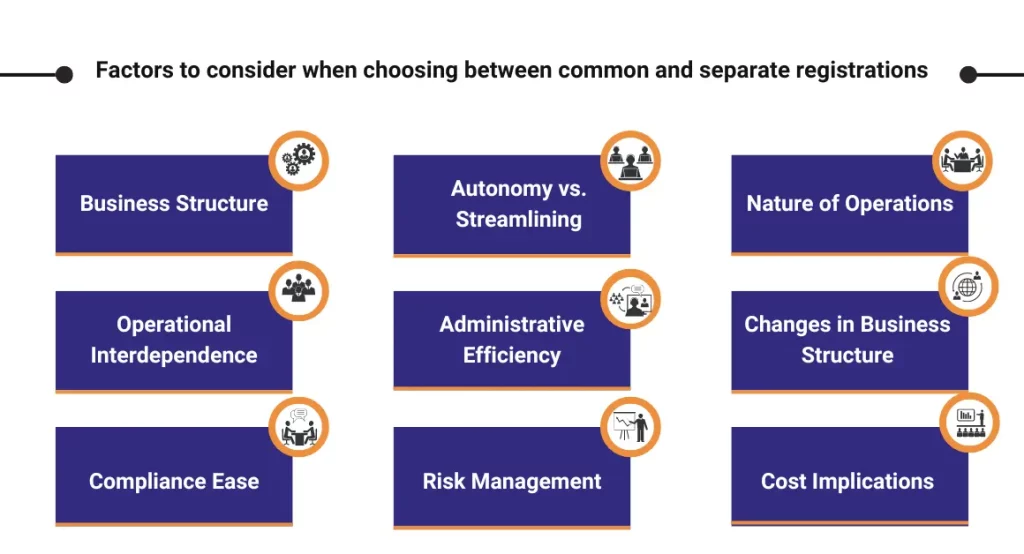
Factors to consider when choosing between common and separate registrations
 When deciding between Common and Separate NRT GST Registrations, several factors should be considered. Here are the key factors:
When deciding between Common and Separate NRT GST Registrations, several factors should be considered. Here are the key factors:
- Business Structure:
- Operational Interdependence:
- Compliance Ease:
- Autonomy vs. Streamlining:
- Administrative Efficiency:
- Risk Management:
- Nature of Operations:
- Changes in Business Structure:
- Cost Implications:
- Legal and Regulatory Considerations:
Impact of registration choice on tax liability and compliance
The choice between Common and Separate NRT GST Registrations can significantly impact both tax liability and compliance. Here’s how:Impact on Tax Liability:
-
Common NRT GST Registration:
-
Separate NRT GST Registrations:
Impact on Compliance:
-
Common NRT GST Registration:
-
Separate NRT GST Registrations:
Tailoring NRT GST registration strategy to business needs
Tailoring Non-Resident Tax (NRT) GST registration strategy to business needs involves a thoughtful consideration of various factors. Here are steps and considerations to help customize the strategy:- Understand Business Structure:
- Assess Operational Dynamics:
- Identify Compliance Requirements:
- Consider Autonomy vs. Centralization:
- Evaluate Risk Tolerance:
- Review Tax Liability Implications:
- Adapt to Changes in Business Structure:
- Evaluate Administrative Efficiencies:
- Customize Reporting and Communication:
- Consider Industry Regulations:
- Assess Cost Implications:
- Seek Professional Advice:
Conclusion:
In conclusion, choosing between common and separate registrations involves weighing the advantages and disadvantages, considering factors like business structure and operational dynamics, and tailoring the strategy to meet specific business needs. The decision significantly impacts tax liability, compliance, and overall efficiency, making it crucial for businesses to carefully evaluate their unique circumstances before making a choice. Also Read: GST: Everything You Need To KnowFAQ’s
-
What is the difference between Common NRT GST registration and Separate Registrations?
-
What are the advantages of Common NRT GST registration?
-
What are the disadvantages of Common NRT GST registration?
-
What are the benefits of Separate NRT GST registrations?
-
What are the drawbacks of Separate NRT GST registrations?
-
What factors should businesses consider when choosing between Common and Separate NRT GST registrations?
-
How does the choice of registration impact tax liability?
-
How does the choice of registration impact compliance?
-
How can businesses tailor NRT GST registration strategy to their needs?
-
What is the importance of industry regulations in tailoring a registration strategy?
Explore pros and cons of NRT GST registration types to optimize your compliance.

Anjali Panda
Senior Content Writer
Anjali Panda, a skilled wordsmith and literature enthusiast, earned her bachelor's degree in English Language and Literature from KiiT University. Her Highest Qualification Holding an MBA in Finance, she effortlessly blends academic knowledge with practical insights in her finance-centric content. Presently, Anjali is leveraging her financial expertise at BitWale, a startup, where she plays a pivotal role in optimizing the company's overall financial operations
